Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state
- PMID: 21106759
- PMCID: PMC3003124
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.1016071107
Histone H3K27ac separates active from poised enhancers and predicts developmental state
Abstract
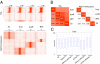
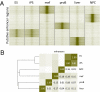
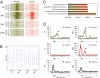
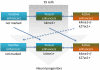
Developmental programs are controlled by transcription factors and chromatin regulators, which maintain specific gene expression programs through epigenetic modification of the genome. These regulatory events at enhancers contribute to the specific gene expression programs that determine cell state and the potential for differentiation into new cell types. Although enhancer elements are known to be associated with certain histone modifications and transcription factors, the relationship of these modifications to gene expression and developmental state has not been clearly defined. Here we interrogate the epigenetic landscape of enhancer elements in embryonic stem cells and several adult tissues in the mouse. We find that histone H3K27ac distinguishes active enhancers from inactive/poised enhancer elements containing H3K4me1 alone. This indicates that the amount of actively used enhancers is lower than previously anticipated. Furthermore, poised enhancer networks provide clues to unrealized developmental programs. Finally, we show that enhancers are reset during nuclear reprogramming.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



Comment in
-
Unraveling the score of the enhancer symphony.Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010 Dec 14;107(50):21240-1. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1016297108. Epub 2010 Dec 6. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2010. PMID: 21135244 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 5-RO1-CA87869/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA042063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30-CA14051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-R37-CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R37 HD045022/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01-CA42063/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA084198/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA014051/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5-RO1-HDO45022/PHS HHS/United States
- R01 HG002668/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA087869/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

