Evaluation of Gremlin-1 as a therapeutic target in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
- PMID: 39361025
- PMCID: PMC11449483
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.95185
Evaluation of Gremlin-1 as a therapeutic target in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis
Abstract
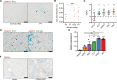
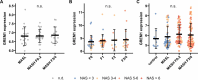
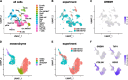
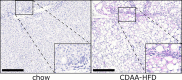
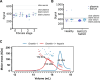
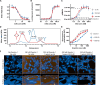
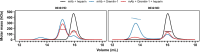
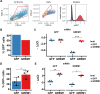
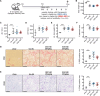
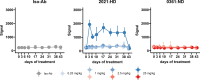
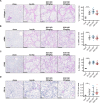
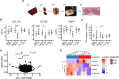
Gremlin-1 has been implicated in liver fibrosis in metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis (MASH) via inhibition of bone morphogenetic protein (BMP) signalling and has thereby been identified as a potential therapeutic target. Using rat in vivo and human in vitro and ex vivo model systems of MASH fibrosis, we show that neutralisation of Gremlin-1 activity with monoclonal therapeutic antibodies does not reduce liver inflammation or liver fibrosis. Still, Gremlin-1 was upregulated in human and rat MASH fibrosis, but expression was restricted to a small subpopulation of COL3A1/THY1+ myofibroblasts. Lentiviral overexpression of Gremlin-1 in LX-2 cells and primary hepatic stellate cells led to changes in BMP-related gene expression, which did not translate to increased fibrogenesis. Furthermore, we show that Gremlin-1 binds to heparin with high affinity, which prevents Gremlin-1 from entering systemic circulation, prohibiting Gremlin-1-mediated organ crosstalk. Overall, our findings suggest a redundant role for Gremlin-1 in the pathogenesis of liver fibrosis, which is unamenable to therapeutic targeting.
Keywords: Gremlin-1; NAFLD; bone morphogenetic proteins; human; liver fibrosis; medicine; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatohepatitis; metabolic dysfunction-associated steatotic liver disease; mouse; rat.
© 2024, Horn et al.
Conflict of interest statement
PH Research funding from Novo Nordisk through the University of Birmingham. Research grant from MSD for research not related to this manuscript. Payment from Orphalan for lecture presentation and travel support and conference attendance fee from IPSEN, JN, BV, EG, AH, FZ, HD, SP, PN, MR, JF Employee of Novo Nordisk A/S. Holding stocks of Novo Nordisk A/S, KA, MF Employee of Novo Nordisk A/S. Holding stocks of Novo Nordisk A/S, Genmab A/S and ALK Abello A/S. Involved in a planned patent indirectly related to MASH, but with no direct relation to this manuscript, MV, MW, MR, ES, EN No competing interests declared, LG Consulting fees and payment or honoraria for lectures, presentations or manuscript writing from: Novo Nordisk, Pfizer, Gilead, AstraZeneca, Norgine, Sobi, Becton Dickinson, Alexion and Vingmed, PL, CW Funding from Novo Nordisk through the University of Birmingham, PN Consulting and honoraria for Boehringer Ingelheim, Novo Nordisk, Intercept, Gilead, Poxel Pharmaceuticals, BMS, Pfizer, Sun Pharma, Madrigal, Eli, Lilly and GSK on behalf of the University of Birmingham. Research grants from Novo Nordisk and Boehringer Ingelheim
Figures


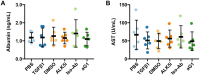
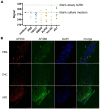
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2024.01.03.574043
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.95185.1
References
-
- Afgan E, Baker D, van den Beek M, Blankenberg D, Bouvier D, Čech M, Chilton J, Clements D, Coraor N, Eberhard C, Grüning B, Guerler A, Hillman-Jackson J, Von Kuster G, Rasche E, Soranzo N, Turaga N, Taylor J, Nekrutenko A, Goecks J. The galaxy platform for accessible, reproducible and collaborative biomedical analyses: 2016 update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2016;44:W3–W10. doi: 10.1093/nar/gkw343. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Baboota RK, Rawshani A, Bonnet L, Li X, Yang H, Mardinoglu A, Tchkonia T, Kirkland JL, Hoffmann A, Dietrich A, Boucher J, Blüher M, Smith U. BMP4 and Gremlin 1 regulate hepatic cell senescence during clinical progression of NAFLD/NASH. Nature Metabolism. 2022;4:1007–1021. doi: 10.1038/s42255-022-00620-x. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Barrett T, Wilhite SE, Ledoux P, Evangelista C, Kim IF, Tomashevsky M, Marshall KA, Phillippy KH, Sherman PM, Holko M, Yefanov A, Lee H, Zhang N, Robertson CL, Serova N, Davis S, Soboleva A. NCBI GEO: archive for functional genomics data sets--update. Nucleic Acids Research. 2013;41:D991–D995. doi: 10.1093/nar/gks1193. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

