Nlrc3 signaling is indispensable for hematopoietic stem cell emergence via Notch signaling in vertebrates
- PMID: 38172511
- PMCID: PMC10764762
- DOI: 10.1038/s41467-023-44251-6
Nlrc3 signaling is indispensable for hematopoietic stem cell emergence via Notch signaling in vertebrates
Abstract
Hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells generate all the lineages of blood cells throughout the lifespan of vertebrates. The emergence of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells is finely tuned by a variety of signaling pathways. Previous studies have revealed the roles of pattern-recognition receptors such as Toll-like receptors and RIG-I-like receptors in hematopoiesis. In this study, we find that Nlrc3, a nucleotide-binding domain leucine-rich repeat containing family gene, is highly expressed in hematopoietic differentiation stages in vivo and vitro and is required in hematopoiesis in zebrafish. Mechanistically, nlrc3 activates the Notch pathway and the downstream gene of Notch hey1. Furthermore, NF-kB signaling acts upstream of nlrc3 to enhance its transcriptional activity. Finally, we find that Nlrc3 signaling is conserved in the regulation of murine embryonic hematopoiesis. Taken together, our findings uncover an indispensable role of Nlrc3 signaling in hematopoietic stem and progenitor cell emergence and provide insights into inflammation-related hematopoietic ontogeny and the in vitro expansion of hematopoietic stem and progenitor cells.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
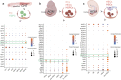

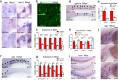

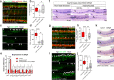
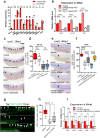

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- 82130003/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82200233/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82100123/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82200255/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
- 82222003/National Natural Science Foundation of China (National Science Foundation of China)
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

