Essential function of transmembrane transcription factor MYRF in promoting transcription of miRNA lin-4 during C. elegans development
- PMID: 38963411
- PMCID: PMC11223767
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.89903
Essential function of transmembrane transcription factor MYRF in promoting transcription of miRNA lin-4 during C. elegans development
Abstract
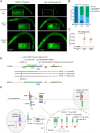
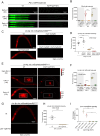
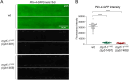
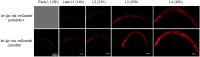
Precise developmental timing control is essential for organism formation and function, but its mechanisms are unclear. In C. elegans, the microRNA lin-4 critically regulates developmental timing by post-transcriptionally downregulating the larval-stage-fate controller LIN-14. However, the mechanisms triggering the activation of lin-4 expression toward the end of the first larval stage remain unknown. We demonstrate that the transmembrane transcription factor MYRF-1 is necessary for lin-4 activation. MYRF-1 is initially localized on the cell membrane, and its increased cleavage and nuclear accumulation coincide with lin-4 expression timing. MYRF-1 regulates lin-4 expression cell-autonomously and hyperactive MYRF-1 can prematurely drive lin-4 expression in embryos and young first-stage larvae. The tandem lin-4 promoter DNA recruits MYRF-1GFP to form visible loci in the nucleus, suggesting that MYRF-1 directly binds to the lin-4 promoter. Our findings identify a crucial link in understanding developmental timing regulation and establish MYRF-1 as a key regulator of lin-4 expression.
Keywords: C. elegans; DD synaptic rewiring; MYRF-2; PAN-1; dauer; developmental biology; intramolecular chaperone; self-cleavage.
© 2023, Xu et al.
Conflict of interest statement
ZX, ZW, LW, YQ No competing interests declared
Figures
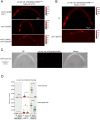
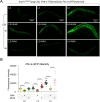
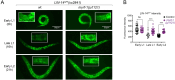
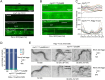
Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.06.22.546200
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.89903.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.89903.2
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.89903.3
References
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Dryad/10.5061/dryad.tqjq2bw71
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

