Analyses of translation factors Dbp1 and Ded1 reveal the cellular response to heat stress to be separable from stress granule formation
- PMID: 39675003
- PMCID: PMC11759133
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2024.115059
Analyses of translation factors Dbp1 and Ded1 reveal the cellular response to heat stress to be separable from stress granule formation
Abstract
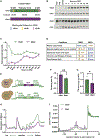
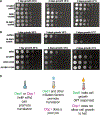
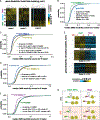
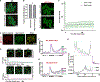
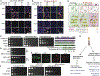
Ded1 and Dbp1 are paralogous conserved DEAD-box ATPases involved in translation initiation in yeast. In long-term starvation states, Dbp1 expression increases and Ded1 decreases, whereas in cycling mitotic cells, Dbp1 is absent. Inserting DBP1 in place of DED1 cannot replace Ded1 function in supporting mitotic translation, partly due to inefficient translation of the DBP1 coding region. Global translation measurements, activity of mRNA-tethered proteins, and growth assays show that-even at matched protein levels-Ded1 is better than Dbp1 at activating translation, especially for mRNAs with structured 5' leaders. Heat-stressed cells normally downregulate translation of structured housekeeping transcripts and halt growth, but neither occurs in Dbp1-expressing cells. This failure to halt growth in response to heat is not based on deficient stress granule formation or failure to reduce bulk translation. Rather, it depends on heat-triggered loss of Ded1 function mediated by an 11-amino-acid interval within its intrinsically disordered C terminus.
Keywords: CP: Molecular biology; DDX3; DEAD-box helicase; Dbp1; Ded1; Translation; heat stress; ribosome profiling; stress granules; translation initiation.
Copyright © 2024 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Conflict of interest statement
Declaration of interests The authors declare no competing interests.
Figures
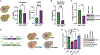

References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

