Human mediator subunit MED26 functions as a docking site for transcription elongation factors
- PMID: 21729782
- PMCID: PMC3145325
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2011.06.005
Human mediator subunit MED26 functions as a docking site for transcription elongation factors
Abstract
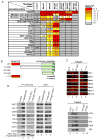
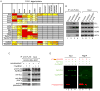
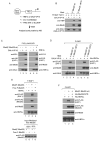
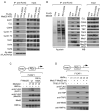
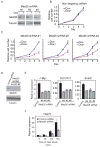
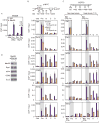
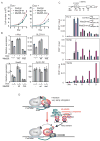
Promoter-proximal pausing by initiated RNA polymerase II (Pol II) and regulated release of paused polymerase into productive elongation has emerged as a major mechanism of transcription activation. Reactivation of paused Pol II correlates with recruitment of super-elongation complexes (SECs) containing ELL/EAF family members, P-TEFb, and other proteins, but the mechanism of their recruitment is an unanswered question. Here, we present evidence for a role of human Mediator subunit MED26 in this process. We identify in the conserved N-terminal domain of MED26 overlapping docking sites for SEC and a second ELL/EAF-containing complex, as well as general initiation factor TFIID. In addition, we present evidence consistent with the model that MED26 can function as a molecular switch that interacts first with TFIID in the Pol II initiation complex and then exchanges TFIID for complexes containing ELL/EAF and P-TEFb to facilitate transition of Pol II into the elongation stage of transcription.
Copyright © 2011 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Adelman K, Marr MT, Werner J, Saunders A, Ni Z, Andrulis ED, Lis JT. Efficient release from promoter-proximal stall sites requires transcript cleavage factor TFIIS. Mol Cell. 2005;17:103–112. - PubMed
-
- Andrau JC, van de PL, Lijnzaad P, Bijma T, Koerkamp MG, van de PJ, Werner M, Holstege FC. Genome-wide location of the coactivator mediator: Binding without activation and transient Cdk8 interaction on DNA. Mol Cell. 2006;22:179–192. - PubMed
-
- Banks CA, Kong SE, Spahr H, Florens L, Martin-Brown S, Washburn MP, Conaway JW, Mushegian A, Conaway RC. Identification and Characterization of a Schizosaccharomyces pombe RNA Polymerase II Elongation Factor with Similarity to the Metazoan Transcription Factor ELL. J Biol Chem. 2007;282:5761–5769. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

