p100 Deficiency is insufficient for full activation of the alternative NF-κB pathway: TNF cooperates with p52-RelB in target gene transcription
- PMID: 22880094
- PMCID: PMC3412832
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0042741
p100 Deficiency is insufficient for full activation of the alternative NF-κB pathway: TNF cooperates with p52-RelB in target gene transcription
Abstract
Background: Constitutive activation of the alternative NF-κB pathway leads to marginal zone B cell expansion and disorganized spleen microarchitecture. Furthermore, uncontrolled alternative NF-κB signaling may result in the development and progression of cancer. Here, we focused on the question how does the constitutive alternative NF-κB signaling exert its effects in these malignant processes.
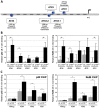
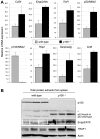
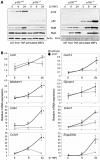
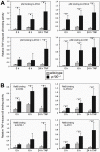
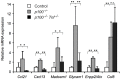
Methodology/principal findings: To explore the consequences of unrestricted alternative NF-κB activation on genome-wide transcription, we compared gene expression profiles of wild-type and NF-κB2/p100-deficient (p100(-/-)) primary mouse embryonic fibroblasts (MEFs) and spleens. Microarray experiments revealed only 73 differentially regulated genes in p100(-/-) vs. wild-type MEFs. Chromatin immunoprecipitation (ChIP) assays showed in p100(-/-) MEFs direct binding of p52 and RelB to the promoter of the Enpp2 gene encoding ENPP2/Autotaxin, a protein with an important role in lymphocyte homing and cell migration. Gene ontology analysis revealed upregulation of genes with anti-apoptotic/proliferative activity (Enpp2/Atx, Serpina3g, Traf1, Rrad), chemotactic/locomotory activity (Enpp2/Atx, Ccl8), and lymphocyte homing activity (Enpp2/Atx, Cd34). Most importantly, biochemical and gene expression analyses of MEFs and spleen, respectively, indicated a marked crosstalk between classical and alternative NF-κB pathways.
Conclusions/significance: Our results show that p100 deficiency alone was insufficient for full induction of genes regulated by the alternative NF-κB pathway. Moreover, alternative NF-κB signaling strongly synergized both in vitro and in vivo with classical NF-κB activation, thereby extending the number of genes under the control of the p100 inhibitor of the alternative NF-κB signaling pathway.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures

References
-
- Ghosh S, Karin M (2002) Missing pieces in the NF-kappaB puzzle. Cell 109 Suppl: S81–96. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2004) Signaling to NF-kappaB. Genes Dev 18: 2195–2224. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, Ghosh S (2008) Shared principles in NF-kappaB signaling. Cell 132: 344–362. - PubMed
-
- Hayden MS, West AP, Ghosh S (2006) NF-kappaB and the immune response. Oncogene 25: 6758–6780. - PubMed
-
- Vallabhapurapu S, Karin M (2009) Regulation and function of NF-kappaB transcription factors in the immune system. Annu Rev Immunol 27: 693–733. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Miscellaneous
