Mammalian X upregulation is associated with enhanced transcription initiation, RNA half-life, and MOF-mediated H4K16 acetylation
- PMID: 23523075
- PMCID: PMC3662796
- DOI: 10.1016/j.devcel.2013.01.028
Mammalian X upregulation is associated with enhanced transcription initiation, RNA half-life, and MOF-mediated H4K16 acetylation
Abstract
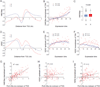
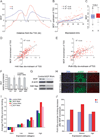
X upregulation in mammals increases levels of expressed X-linked transcripts to compensate for autosomal biallelic expression. Here, we present molecular mechanisms that enhance X expression at transcriptional and posttranscriptional levels. Active mouse X-linked promoters are enriched in the initiation form of RNA polymerase II (PolII-S5p) and in specific histone marks, including histone H4 acetylated at lysine 16 (H4K16ac) and histone variant H2AZ. The H4K16 acetyltransferase males absent on the first (MOF), known to mediate the Drosophila X upregulation, is also enriched on the mammalian X. Depletion of MOF or male-specific lethal 1 (MSL1) in mouse ES cells causes a specific decrease in PolII-S5p and in expression of a subset of X-linked genes. Analyses of RNA half-life data sets show increased stability of mammalian X-linked transcripts. Both ancestral X-linked genes, defined as those conserved on chicken autosomes, and newly acquired X-linked genes are upregulated by similar mechanisms but to a different extent, suggesting that subsets of genes are distinctly regulated depending on their evolutionary history.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





Comment in
-
Gene expression: Extra X expression.Nat Rev Genet. 2013 May;14(5):304. doi: 10.1038/nrg3479. Epub 2013 Apr 4. Nat Rev Genet. 2013. PMID: 23552217 No abstract available.
References
-
- Adler DA, Rugarli EI, Lingenfelter PA, Tsuchiya K, Poslinski D, Liggitt HD, Chapman VM, Elliott RW, Ballabio A, Disteche CM. Evidence of evolutionary up-regulation of the single active X chromosome in mammals based on Clc4 expression levels in Mus spretus and Mus musculus. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 1997;94:9244–9248. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Akhtar A, Becker PB. Activation of transcription through histone H4 acetylation by MOF, an acetyltransferase essential for dosage compensation in Drosophila. Mol Cell. 2000;5:367–375. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

