Comparative transcriptomics of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Listeria species
- PMID: 22617957
- PMCID: PMC3377988
- DOI: 10.1038/msb.2012.11
Comparative transcriptomics of pathogenic and non-pathogenic Listeria species
Abstract
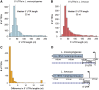
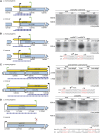
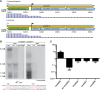
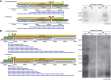
Listeria monocytogenes is a human, food-borne pathogen. Genomic comparisons between L. monocytogenes and Listeria innocua, a closely related non-pathogenic species, were pivotal in the identification of protein-coding genes essential for virulence. However, no comprehensive comparison has focused on the non-coding genome. We used strand-specific cDNA sequencing to produce genome-wide transcription start site maps for both organisms, and developed a publicly available integrative browser to visualize and analyze both transcriptomes in different growth conditions and genetic backgrounds. Our data revealed conservation across most transcripts, but significant divergence between the species in a subset of non-coding RNAs. In L. monocytogenes, we identified 113 small RNAs (33 novel) and 70 antisense RNAs (53 novel), significantly increasing the repertoire of ncRNAs in this species. Remarkably, we identified a class of long antisense transcripts (lasRNAs) that overlap one gene while also serving as the 5' UTR of the adjacent divergent gene. Experimental evidence suggests that lasRNAs transcription inhibits expression of one operon while activating the expression of another. Such a lasRNA/operon structure, that we named 'excludon', might represent a novel form of regulation in bacteria.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Figures


Comment in
-
Bacterial Transcription: Introducing the excludon.Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012 Jun 11;10(7):443. doi: 10.1038/nrmicro2822. Nat Rev Microbiol. 2012. PMID: 22683879 No abstract available.
References
-
- Avrani S, Wurtzel O, Sharon I, Sorek R, Lindell D (2011) Genomic island variability facilitates Prochlorococcus-virus coexistence. Nature 474: 604–608 - PubMed
-
- Brantl S (2007) Regulatory mechanisms employed by cis-encoded antisense RNAs. Curr Opin Microbiol 10: 102–109 - PubMed
-
- Cossart P, Toledo-Arana A (2008) Listeria monocytogenes, a unique model in infection biology: an overview. Microbes Infect 10: 1041–1050 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

