required to maintain repression2 is a novel protein that facilitates locus-specific paramutation in maize
- PMID: 22562610
- PMCID: PMC3442568
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.112.097618
required to maintain repression2 is a novel protein that facilitates locus-specific paramutation in maize
Abstract
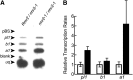
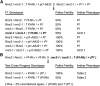
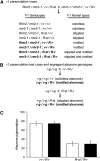
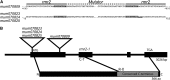
Meiotically heritable epigenetic changes in gene regulation known as paramutations are facilitated by poorly understood trans-homolog interactions. Mutations affecting paramutations in maize (Zea mays) identify components required for the accumulation of 24-nucleotide RNAs. Some of these components have Arabidopsis thaliana orthologs that are part of an RNA-directed DNA methylation (RdDM) pathway. It remains unclear if small RNAs actually mediate paramutations and whether the maize-specific molecules identified to date define a mechanism distinct from RdDM. Here, we identify a novel protein required for paramutation at the maize purple plant1 locus. This required to maintain repression2 (RMR2) protein represents the founding member of a plant-specific clade of predicted proteins. We show that RMR2 is required for transcriptional repression at the Pl1-Rhoades haplotype, for accumulation of 24-nucleotide RNA species, and for maintenance of a 5-methylcytosine pattern distinct from that maintained by RNA polymerase IV. Genetic tests indicate that RMR2 is not required for paramutation occurring at the red1 locus. These results distinguish the paramutation-type mechanisms operating at specific haplotypes. The RMR2 clade of proteins provides a new entry point for understanding the diversity of epigenomic control operating in higher plants.
Figures
References
-
- Alleman M., Sidorenko L., McGinnis K., Seshadri V., Dorweiler J.E., White J., Sikkink K., Chandler V.L. (2006). An RNA-dependent RNA polymerase is required for paramutation in maize. Nature 442: 295–298 - PubMed
-
- Altschul S.F., Gish W., Miller W., Myers E.W., Lipman D.J. (1990). Basic local alignment search tool. J. Mol. Biol. 215: 403–410 - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

