An overlapping protein-coding region in influenza A virus segment 3 modulates the host response
- PMID: 22745253
- PMCID: PMC3552242
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1222213
An overlapping protein-coding region in influenza A virus segment 3 modulates the host response
Abstract
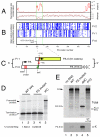
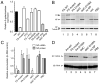
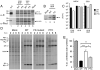
Influenza A virus (IAV) infection leads to variable and imperfectly understood pathogenicity. We report that segment 3 of the virus contains a second open reading frame ("X-ORF"), accessed via ribosomal frameshifting. The frameshift product, termed PA-X, comprises the endonuclease domain of the viral PA protein with a C-terminal domain encoded by the X-ORF and functions to repress cellular gene expression. PA-X also modulates IAV virulence in a mouse infection model, acting to decrease pathogenicity. Loss of PA-X expression leads to changes in the kinetics of the global host response, which notably includes increases in inflammatory, apoptotic, and T lymphocyte-signaling pathways. Thus, we have identified a previously unknown IAV protein that modulates the host response to infection, a finding with important implications for understanding IAV pathogenesis.
Figures
Comment in
-
Virology. Frameshifting to PA-X influenza.Science. 2012 Jul 13;337(6091):164-5. doi: 10.1126/science.1225539. Science. 2012. PMID: 22798590 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Palese S, M.L. P. In: Fields Virology. Knipe DM, Howley PM, editors. Lippincott Williams & Wilkins, Philadelphia; 2007. p. 1647.
-
- Yuan P, et al. Crystal structure of an avian influenza polymerase PA(N) reveals an endonuclease active site. Nature. 2009;458:909. - PubMed
-
- Dias A, et al. The cap-snatching endonuclease of influenza virus polymerase resides in the PA subunit. Nature. 2009;458:914. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

