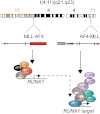
RUNX1 is a key target in t(4;11) leukemias that contributes to gene activation through an AF4-MLL complex interaction
- PMID: 23352661
- PMCID: PMC3607232
- DOI: 10.1016/j.celrep.2012.12.016
RUNX1 is a key target in t(4;11) leukemias that contributes to gene activation through an AF4-MLL complex interaction
Abstract
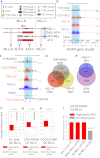
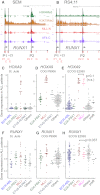
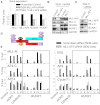
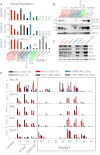
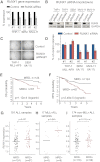
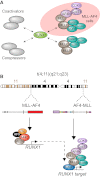
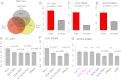
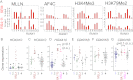
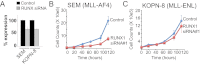
The Mixed Lineage Leukemia (MLL) protein is an important epigenetic regulator required for the maintenance of gene activation during development. MLL chromosomal translocations produce novel fusion proteins that cause aggressive leukemias in humans. Individual MLL fusion proteins have distinct leukemic phenotypes even when expressed in the same cell type, but how this distinction is delineated on a molecular level is poorly understood. Here, we highlight a unique molecular mechanism whereby the RUNX1 gene is directly activated by MLL-AF4 and the RUNX1 protein interacts with the product of the reciprocal AF4-MLL translocation. These results support a mechanism of transformation whereby two oncogenic fusion proteins cooperate by activating a target gene and then modulating the function of its downstream product.
Copyright © 2013 The Authors. Published by Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Akalin A., Garrett-Bakelman F.E., Kormaksson M., Busuttil J., Zhang L., Khrebtukova I., Milne T.A., Huang Y., Biswas D., Hess J.L. Base-pair resolution DNA methylation sequencing reveals profoundly divergent epigenetic landscapes in acute myeloid leukemia. PLoS Genet. 2012;8:e1002781. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Bardini M., Spinelli R., Bungaro S., Mangano E., Corral L., Cifola I., Fazio G., Giordan M., Basso G., De Rossi G. DNA copy-number abnormalities do not occur in infant ALL with t(4;11)/MLL-AF4. Leukemia. 2010;24:169–176. - PubMed
-
- Bardini M., Galbiati M., Lettieri A., Bungaro S., Gorletta T.A., Biondi A., Cazzaniga G. Implementation of array based whole-genome high-resolution technologies confirms the absence of secondary copy-number alterations in MLL-AF4-positive infant ALL patients. Leukemia. 2011;25:175–178. - PubMed
-
- Benedikt A., Baltruschat S., Scholz B., Bursen A., Arrey T.N., Meyer B., Varagnolo L., Müller A.M., Karas M., Dingermann T., Marschalek R. The leukemogenic AF4-MLL fusion protein causes P-TEFb kinase activation and altered epigenetic signatures. Leukemia. 2011;25:135–144. - PubMed
Supplemental References
-
- Bolstad, B.M., Irizarry, R.A., Astrand, M., and Speed, T.P. (2003). A comparison of normalization methods for high density oligonucleotide array data based on variance and bias. Bioinformatics 19, 185–193. - PubMed
-
- Borowitz, M.J., Devidas, M., Hunger, S.P., Bowman, W.P., Carroll, A.J., Carroll, W.L., Linda, S., Martin, P.L., Pullen, D.J., Viswanatha, D., et al. (2008). Clinical significance of minimal residual disease in childhood acute lymphoblastic leukemia and its relationship to other prognostic factors: a Children's Oncology Group study. Blood 111, 5477–5485. - PMC - PubMed
-
- Chen, S., Xue, Y., Zhang, X., Wu, Y., Pan, J., Wang, Y., and Ceng, J. (2005). A new human acute monocytic leukemia cell line SHI-1 with t(6;11)(q27;q23), p53 gene alterations and high tumorigenicity in nude mice. Haematologica 90, 766–775. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

