Hira-dependent histone H3.3 deposition facilitates PRC2 recruitment at developmental loci in ES cells
- PMID: 24074864
- PMCID: PMC3838450
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.061
Hira-dependent histone H3.3 deposition facilitates PRC2 recruitment at developmental loci in ES cells
Abstract
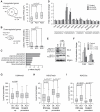
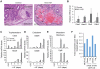
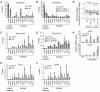
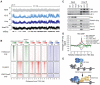
Polycomb repressive complex 2 (PRC2) regulates gene expression during lineage specification through trimethylation of lysine 27 on histone H3 (H3K27me3). In Drosophila, polycomb binding sites are dynamic chromatin regions enriched with the histone variant H3.3. Here, we show that, in mouse embryonic stem cells (ESCs), H3.3 is required for proper establishment of H3K27me3 at the promoters of developmentally regulated genes. Upon H3.3 depletion, these promoters show reduced nucleosome turnover measured by deposition of de novo synthesized histones and reduced PRC2 occupancy. Further, we show H3.3-dependent interaction of PRC2 with the histone chaperone, Hira, and that Hira localization to chromatin requires H3.3. Our data demonstrate the importance of H3.3 in maintaining a chromatin landscape in ESCs that is important for proper gene regulation during differentiation. Moreover, our findings support the emerging notion that H3.3 has multiple functions in distinct genomic locations that are not always correlated with an "active" chromatin state.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures


References
-
- Bernstein BE, Mikkelsen TS, Xie X, Kamal M, Huebert DJ, Cuff J, Fry B, Meissner A, Wernig M, Plath K, et al. A bivalent chromatin structure marks key developmental genes in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2006;125:315–326. - PubMed
-
- Couldrey C, Carlton MB, Nolan PM, Colledge WH, Evans MJ. A retroviral gene trap insertion into the histone 3.3A gene causes partial neonatal lethality, stunted growth, neuromuscular deficits and male sub-fertility in transgenic mice. Hum Mol Genet. 1999;8:2489–2495. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

