MYCN and HDAC2 cooperate to repress miR-183 signaling in neuroblastoma
- PMID: 23625969
- PMCID: PMC3695529
- DOI: 10.1093/nar/gkt346
MYCN and HDAC2 cooperate to repress miR-183 signaling in neuroblastoma
Abstract
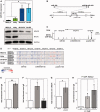
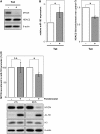
MYCN is a master regulator controlling many processes necessary for tumor cell survival. Here, we unravel a microRNA network that causes tumor suppressive effects in MYCN-amplified neuroblastoma cells. In profiling studies, histone deacetylase (HDAC) inhibitor treatment most strongly induced miR-183. Enforced miR-183 expression triggered apoptosis, and inhibited anchorage-independent colony formation in vitro and xenograft growth in mice. Furthermore, the mechanism of miR-183 induction was found to contribute to the cell death phenotype induced by HDAC inhibitors. Experiments to identify the HDAC(s) involved in miR-183 transcriptional regulation showed that HDAC2 depletion induced miR-183. HDAC2 overexpression reduced miR-183 levels and counteracted the induction caused by HDAC2 depletion or HDAC inhibitor treatment. MYCN was found to recruit HDAC2 in the same complexes to the miR-183 promoter, and HDAC2 depletion enhanced promoter-associated histone H4 pan-acetylation, suggesting epigenetic changes preceded transcriptional activation. These data reveal miR-183 tumor suppressive properties in neuroblastoma that are jointly repressed by MYCN and HDAC2, and suggest a novel way to bypass MYCN function.
Figures





References
-
- Brodeur GM. Neuroblastoma: biological insights into a clinical enigma. Nat. Rev. Cancer. 2003;3:203–216. - PubMed
-
- Schwab M, Westermann F, Hero B, Berthold F. Neuroblastoma: biology and molecular and chromosomal pathology. Lancet Oncol. 2003;4:472–480. - PubMed
-
- Westermark UK, Wilhelm M, Frenzel A, Henriksson MA. The MYCN oncogene and differentiation in neuroblastoma. Semin. Cancer Biol. 2011;21:256–266. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

