Organ-level quorum sensing directs regeneration in hair stem cell populations
- PMID: 25860610
- PMCID: PMC4393531
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.02.016
Organ-level quorum sensing directs regeneration in hair stem cell populations
Abstract
Coordinated organ behavior is crucial for an effective response to environmental stimuli. By studying regeneration of hair follicles in response to patterned hair plucking, we demonstrate that organ-level quorum sensing allows coordinated responses to skin injury. Plucking hair at different densities leads to a regeneration of up to five times more neighboring, unplucked resting hairs, indicating activation of a collective decision-making process. Through data modeling, the range of the quorum signal was estimated to be on the order of 1 mm, greater than expected for a diffusible molecular cue. Molecular and genetic analysis uncovered a two-step mechanism, where release of CCL2 from injured hairs leads to recruitment of TNF-α-secreting macrophages, which accumulate and signal to both plucked and unplucked follicles. By coupling immune response with regeneration, this mechanism allows skin to respond predictively to distress, disregarding mild injury, while meeting stronger injury with full-scale cooperative activation of stem cells.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures

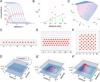
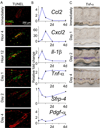



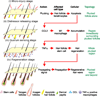
Comment in
-
A collective path toward regeneration.Cell. 2015 Apr 9;161(2):195-6. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2015.03.039. Cell. 2015. PMID: 25860601
References
-
- Ansell DM, Kloepper JE, Thomason HA, Paus R, Hardman MJ. Exploring the "hair growth-wound healing connection": anagen phase promotes wound re-epithelialization. J. Invest. Dermatol. 2011;131:518–528. - PubMed
-
- Bassler BL. Small talk. Cell-to-cell communication in bacteria. Cell. 2002;109:421–424. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R37 AR060306/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01DE17449/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE017449/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR067273/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR067273/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01-AR42177/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR 47364/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR060306/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50 GM076516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR042177/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AR047364/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
- P50-GM076516/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- AR60306/AR/NIAMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

