The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome
- PMID: 23828888
- PMCID: PMC3778663
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1237973
The Xist lncRNA exploits three-dimensional genome architecture to spread across the X chromosome
Abstract
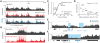
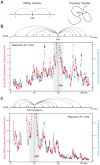
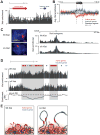
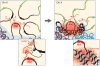
Many large noncoding RNAs (lncRNAs) regulate chromatin, but the mechanisms by which they localize to genomic targets remain unexplored. We investigated the localization mechanisms of the Xist lncRNA during X-chromosome inactivation (XCI), a paradigm of lncRNA-mediated chromatin regulation. During the maintenance of XCI, Xist binds broadly across the X chromosome. During initiation of XCI, Xist initially transfers to distal regions across the X chromosome that are not defined by specific sequences. Instead, Xist identifies these regions by exploiting the three-dimensional conformation of the X chromosome. Xist requires its silencing domain to spread across actively transcribed regions and thereby access the entire chromosome. These findings suggest a model in which Xist coats the X chromosome by searching in three dimensions, modifying chromosome structure, and spreading to newly accessible locations.
Figures


Comment in
-
Molecular biology. Long noncoding RNAs Xist in three dimensions.Science. 2013 Aug 16;341(6147):720-1. doi: 10.1126/science.1243257. Science. 2013. PMID: 23950517 No abstract available.
-
X-inactivation: Xist RNA uses chromosome contacts to coat the X.Curr Biol. 2014 Jan 20;24(2):R80-R82. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.11.052. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24456982 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Carninci P, et al. The transcriptional landscape of the mammalian genome. Science. 2005 Sep 2;309:1559. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

