Mono-methylated histones control PARP-1 in chromatin and transcription
- PMID: 38690995
- PMCID: PMC11062633
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.91482
Mono-methylated histones control PARP-1 in chromatin and transcription
Abstract
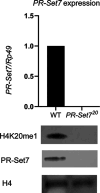
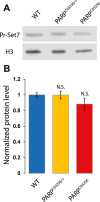
PARP-1 is central to transcriptional regulation under both normal and stress conditions, with the governing mechanisms yet to be fully understood. Our biochemical and ChIP-seq-based analyses showed that PARP-1 binds specifically to active histone marks, particularly H4K20me1. We found that H4K20me1 plays a critical role in facilitating PARP-1 binding and the regulation of PARP-1-dependent loci during both development and heat shock stress. Here, we report that the sole H4K20 mono-methylase, pr-set7, and parp-1 Drosophila mutants undergo developmental arrest. RNA-seq analysis showed an absolute correlation between PR-SET7- and PARP-1-dependent loci expression, confirming co-regulation during developmental phases. PARP-1 and PR-SET7 are both essential for activating hsp70 and other heat shock genes during heat stress, with a notable increase of H4K20me1 at their gene body. Mutating pr-set7 disrupts monomethylation of H4K20 along heat shock loci and abolish PARP-1 binding there. These data strongly suggest that H4 monomethylation is a key triggering point in PARP-1 dependent processes in chromatin.
Keywords: D. melanogaster; H3K27me1; H3K36me1; H3K4me1; H4K20me1; PARP-1; PR-SET7; genetics; genomics.
© 2024, Bamgbose et al.
Conflict of interest statement
GB, GB, NL, AT No competing interests declared
Figures



Update of
- doi: 10.1101/2023.11.22.568326
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91482.1
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91482.2
- doi: 10.7554/eLife.91482.3
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

