Fine tuning of craniofacial morphology by distant-acting enhancers
- PMID: 24159046
- PMCID: PMC3991470
- DOI: 10.1126/science.1241006
Fine tuning of craniofacial morphology by distant-acting enhancers
Abstract
The shape of the human face and skull is largely genetically determined. However, the genomic basis of craniofacial morphology is incompletely understood and hypothesized to involve protein-coding genes, as well as gene regulatory sequences. We used a combination of epigenomic profiling, in vivo characterization of candidate enhancer sequences in transgenic mice, and targeted deletion experiments to examine the role of distant-acting enhancers in craniofacial development. We identified complex regulatory landscapes consisting of enhancers that drive spatially complex developmental expression patterns. Analysis of mouse lines in which individual craniofacial enhancers had been deleted revealed significant alterations of craniofacial shape, demonstrating the functional importance of enhancers in defining face and skull morphology. These results demonstrate that enhancers are involved in craniofacial development and suggest that enhancer sequence variation contributes to the diversity of human facial morphology.
Figures



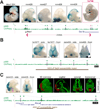
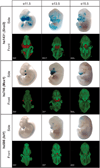
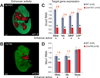

Comment in
-
Development: facial makeup enhancing our looks.Curr Biol. 2014 Jan 6;24(1):R36-R38. doi: 10.1016/j.cub.2013.11.026. Curr Biol. 2014. PMID: 24405678
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- R01 HG003988/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DE021708/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- MC_PC_U127561093/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- R01 DE019638/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG003991/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- 1U01DE020054/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM105202/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- U01DE020060/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DE021708/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DE020060/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- U54HG006997/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- MC_U127561093/MRC_/Medical Research Council/United Kingdom
- U01 DE020054/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- 1R01DE01963/DE/NIDCR NIH HHS/United States
- R01HG003988/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- U54 HG006997/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 HG003991/HG/NHGRI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

