NCoR repression of LXRs restricts macrophage biosynthesis of insulin-sensitizing omega 3 fatty acids
- PMID: 24074869
- PMCID: PMC4131699
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cell.2013.08.054
NCoR repression of LXRs restricts macrophage biosynthesis of insulin-sensitizing omega 3 fatty acids
Abstract
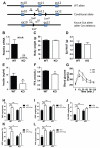
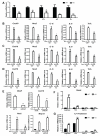
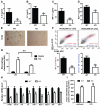
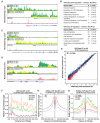
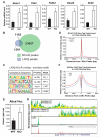
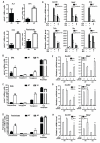
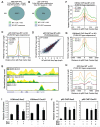
Macrophage-mediated inflammation is a major contributor to obesity-associated insulin resistance. The corepressor NCoR interacts with inflammatory pathway genes in macrophages, suggesting that its removal would result in increased activity of inflammatory responses. Surprisingly, we find that macrophage-specific deletion of NCoR instead results in an anti-inflammatory phenotype along with robust systemic insulin sensitization in obese mice. We present evidence that derepression of LXRs contributes to this paradoxical anti-inflammatory phenotype by causing increased expression of genes that direct biosynthesis of palmitoleic acid and ω3 fatty acids. Remarkably, the increased ω3 fatty acid levels primarily inhibit NF-κB-dependent inflammatory responses by uncoupling NF-κB binding and enhancer/promoter histone acetylation from subsequent steps required for proinflammatory gene activation. This provides a mechanism for the in vivo anti-inflammatory insulin-sensitive phenotype observed in mice with macrophage-specific deletion of NCoR. Therapeutic methods to harness this mechanism could lead to a new approach to insulin-sensitizing therapies.
Copyright © 2013 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
References
-
- Bouhlel MA, Derudas B, Rigamonti E, Dievart R, Brozek J, Haulon S, Zawadzki C, Jude B, Torpier G, Marx N, et al. PPARgamma activation primes human monocytes into alternative M2 macrophages with anti-inflammatory properties. Cell Metab. 2007;6:137–143. - PubMed
-
- Brown HA, Henage LG, Preininger AM, Xiang Y, Exton JH. Biochemical analysis of phospholipase D. Methods in enzymology. 2007;434:49–87. - PubMed
-
- Chen JD, Evans RM. A transcriptional co-repressor that interacts with nuclear hormone receptors. Nature. 1995;377:454–457. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- GM069338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- U54 GM069338/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 231138/ERC_/European Research Council/International
- P30 DK063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA023100/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P50 HD012303/HD/NICHD NIH HHS/United States
- R37 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- F32 DK009062/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK033651/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK091183/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-09062/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK074868/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- DK-063491/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

