DJ-1, a cancer- and Parkinson's disease-associated protein, stabilizes the antioxidant transcriptional master regulator Nrf2
- PMID: 17015834
- PMCID: PMC1586179
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0607260103
DJ-1, a cancer- and Parkinson's disease-associated protein, stabilizes the antioxidant transcriptional master regulator Nrf2
Abstract
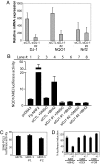
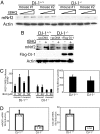
DJ-1/PARK7, a cancer- and Parkinson's disease (PD)-associated protein, protects cells from toxic stresses. However, the functional basis of this protection has remained elusive. We found that loss of DJ-1 leads to deficits in NQO1 [NAD(P)H quinone oxidoreductase 1], a detoxification enzyme. This deficit is attributed to a loss of Nrf2 (nuclear factor erythroid 2-related factor), a master regulator of antioxidant transcriptional responses. DJ-1 stabilizes Nrf2 by preventing association with its inhibitor protein, Keap1, and Nrf2's subsequent ubiquitination. Without intact DJ-1, Nrf2 protein is unstable, and transcriptional responses are thereby decreased both basally and after induction. This effect of DJ-1 on Nrf2 is present in both transformed lines and primary cells across human and mouse species. DJ-1's effect on Nrf2 and subsequent effects on antioxidant responses may explain how DJ-1 affects the etiology of both cancer and PD, which are seemingly disparate disorders. Furthermore, this DJ-1/Nrf2 functional axis presents a therapeutic target in cancer treatment and justifies DJ-1 as a tumor biomarker.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures
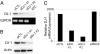

References
-
- Beckman JS, Carson M, Smith CD, Koppenol WH. Nature. 1993;364:584. - PubMed
-
- Bonifati V, Rizzu P, van Baren MJ, Schaap O, Breedveld GJ, Krieger E, Dekker MC, Squitieri F, Ibanez P, Joosse M, et al. Science. 2003;299:256–259. - PubMed
-
- Nagakubo D, Taira T, Kitaura H, Ikeda M, Tamai K, Iguchi-Ariga SM, Ariga H. Biochem Biophys Res Commun. 1997;231:509–513. - PubMed
-
- MacKeigan JP, Clements CM, Lich JD, Pope RM, Hod Y, Ting JP. Cancer Res. 2003;63:6928–6934. - PubMed
-
- Hod Y. J Cell Biochem. 2004;92:1221–1233. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

