Genomic analysis of ADAR1 binding and its involvement in multiple RNA processing pathways
- PMID: 25751603
- PMCID: PMC4355961
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms7355
Genomic analysis of ADAR1 binding and its involvement in multiple RNA processing pathways
Abstract
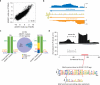
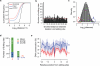
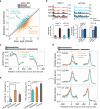
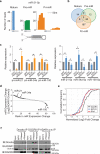
Adenosine deaminases acting on RNA (ADARs) are the primary factors underlying adenosine to inosine (A-to-I) editing in metazoans. Here we report the first global study of ADAR1-RNA interaction in human cells using CLIP-seq. A large number of CLIP sites are observed in Alu repeats, consistent with ADAR1's function in RNA editing. Surprisingly, thousands of other CLIP sites are located in non-Alu regions, revealing functional and biophysical targets of ADAR1 in the regulation of alternative 3' UTR usage and miRNA biogenesis. We observe that binding of ADAR1 to 3' UTRs precludes binding by other factors, causing 3' UTR lengthening. Similarly, ADAR1 interacts with DROSHA and DGCR8 in the nucleus and possibly out-competes DGCR8 in primary miRNA binding, which enhances mature miRNA expression. These functions are dependent on ADAR1's editing activity, at least for a subset of targets. Our study unfolds a broad landscape of the functional roles of ADAR1.
Figures
References
-
- Kawakubo K, Samuel CE. Human RNA-specific adenosine deaminase (ADAR1) gene specifies transcripts that initiate from a constitutively active alternative promoter. Gene. 2000;258:165–172. - PubMed
-
- Melcher T, Maas S, Herb A, Sprengel R, Seeburg PH, Higuchi M. A mammalian RNA editing enzyme. Nature. 1996;379:460–464. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

