Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity
- PMID: 25421927
- PMCID: PMC4263141
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms6488
Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity
Erratum in
-
Erratum: Exosomes secreted by nematode parasites transfer small RNAs to mammalian cells and modulate innate immunity.Nat Commun. 2015 Oct 22;6:8772. doi: 10.1038/ncomms9772. Nat Commun. 2015. PMID: 26490107 Free PMC article. No abstract available.
Abstract
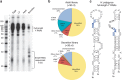
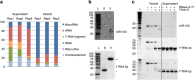
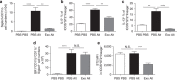
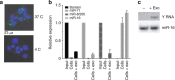
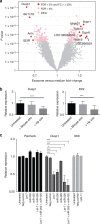
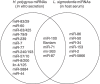
In mammalian systems RNA can move between cells via vesicles. Here we demonstrate that the gastrointestinal nematode Heligmosomoides polygyrus, which infects mice, secretes vesicles containing microRNAs (miRNAs) and Y RNAs as well as a nematode Argonaute protein. These vesicles are of intestinal origin and are enriched for homologues of mammalian exosome proteins. Administration of the nematode exosomes to mice suppresses Type 2 innate responses and eosinophilia induced by the allergen Alternaria. Microarray analysis of mouse cells incubated with nematode exosomes in vitro identifies Il33r and Dusp1 as suppressed genes, and Dusp1 can be repressed by nematode miRNAs based on a reporter assay. We further identify miRNAs from the filarial nematode Litomosoides sigmodontis in the serum of infected mice, suggesting that miRNA secretion into host tissues is conserved among parasitic nematodes. These results reveal exosomes as another mechanism by which helminths manipulate their hosts and provide a mechanistic framework for RNA transfer between animal species.
Figures


References
-
- Blaxter M. L. et al. A molecular evolutionary framework for the phylum Nematoda. Nature 392, 71–75 (1998). - PubMed
-
- Mohrs K., Harris D. P., Lund F. E. & Mohrs M. Systemic dissemination and persistence of Th2 and type 2 cells in response to infection with a strictly enteric nematode parasite. J. Immunol. 175, 5306–5313 (2005). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

