Disruption of DNA-methylation-dependent long gene repression in Rett syndrome
- PMID: 25762136
- PMCID: PMC4480648
- DOI: 10.1038/nature14319
Disruption of DNA-methylation-dependent long gene repression in Rett syndrome
Abstract
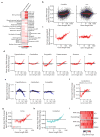
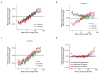
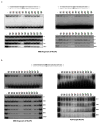
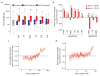
Disruption of the MECP2 gene leads to Rett syndrome (RTT), a severe neurological disorder with features of autism. MECP2 encodes a methyl-DNA-binding protein that has been proposed to function as a transcriptional repressor, but despite numerous mouse studies examining neuronal gene expression in Mecp2 mutants, no clear model has emerged for how MeCP2 protein regulates transcription. Here we identify a genome-wide length-dependent increase in gene expression in MeCP2 mutant mouse models and human RTT brains. We present evidence that MeCP2 represses gene expression by binding to methylated CA sites within long genes, and that in neurons lacking MeCP2, decreasing the expression of long genes attenuates RTT-associated cellular deficits. In addition, we find that long genes as a population are enriched for neuronal functions and selectively expressed in the brain. These findings suggest that mutations in MeCP2 may cause neurological dysfunction by specifically disrupting long gene expression in the brain.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures








Comment in
-
Gene length matters in neurons.Neuron. 2015 Apr 22;86(2):353-5. doi: 10.1016/j.neuron.2015.03.059. Neuron. 2015. PMID: 25905808 Free PMC article.
-
Epigenetics. Exceptional epigenetics in the brain.Science. 2015 Jun 5;348(6239):1094-5. doi: 10.1126/science.aac5832. Science. 2015. PMID: 26045424 Free PMC article.
References
-
- Tudor M, Akbarian S, Chen RZ, Jaenisch R. Transcriptional profiling of a mouse model for Rett syndrome reveals subtle transcriptional changes in the brain. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America. 2002;99:15536–15541. doi: 10.1073/pnas.242566899. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

