Metabolic regulator LKB1 is crucial for Schwann cell-mediated axon maintenance
- PMID: 25195104
- PMCID: PMC4494117
- DOI: 10.1038/nn.3809
Metabolic regulator LKB1 is crucial for Schwann cell-mediated axon maintenance
Abstract
Schwann cells (SCs) promote axonal integrity independently of myelination by poorly understood mechanisms. Current models suggest that SC metabolism is critical for this support function and that SC metabolic deficits may lead to axonal demise. The LKB1-AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) kinase pathway targets several downstream effectors, including mammalian target of rapamycin (mTOR), and is a key metabolic regulator implicated in metabolic diseases. We found through molecular, structural and behavioral characterization of SC-specific mutant mice that LKB1 activity is central to axon stability, whereas AMPK and mTOR in SCs are largely dispensable. The degeneration of axons in LKB1 mutants was most dramatic in unmyelinated small sensory fibers, whereas motor axons were comparatively spared. LKB1 deletion in SCs led to abnormalities in nerve energy and lipid homeostasis and to increased lactate release. The latter acts in a compensatory manner to support distressed axons. LKB1 signaling is essential for SC-mediated axon support, a function that may be dysregulated in diabetic neuropathy.
Conflict of interest statement
R.W.G. has financial relationships with LipoSpectrum and Platomics Inc. The other authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
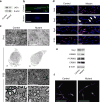
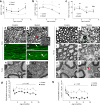
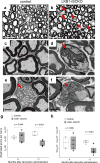
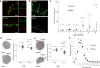
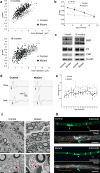
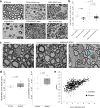
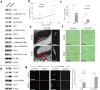
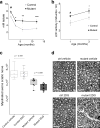
Comment in
-
Glia: Schwann cells provide life support for axons.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014 Nov;15(11):698-9. doi: 10.1038/nrn3840. Epub 2014 Sep 24. Nat Rev Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25248331 No abstract available.
-
Axons hooked to Schwann cell metabolism.Nat Neurosci. 2014 Oct;17(10):1293-5. doi: 10.1038/nn.3825. Nat Neurosci. 2014. PMID: 25254976 No abstract available.
References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P30 NS057105/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 NS040745/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- RF1 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R01 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- R21NS059566/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- 2P01 HL057278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R56 AG013730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK020579/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- P01 HL057278/HL/NHLBI NIH HHS/United States
- R21 NS059566/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- NS087306/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
- AG13730/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- AG0 038036/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- L30 AG038036/AG/NIA NIH HHS/United States
- NS040745/NS/NINDS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

