An AUTS2-Polycomb complex activates gene expression in the CNS
- PMID: 25519132
- PMCID: PMC4323097
- DOI: 10.1038/nature13921
An AUTS2-Polycomb complex activates gene expression in the CNS
Abstract
Naturally occurring variations of Polycomb repressive complex 1 (PRC1) comprise a core assembly of Polycomb group proteins and additional factors that include, surprisingly, autism susceptibility candidate 2 (AUTS2). Although AUTS2 is often disrupted in patients with neuronal disorders, the mechanism underlying the pathogenesis is unclear. We investigated the role of AUTS2 as part of a previously identified PRC1 complex (PRC1-AUTS2), and in the context of neurodevelopment. In contrast to the canonical role of PRC1 in gene repression, PRC1-AUTS2 activates transcription. Biochemical studies demonstrate that the CK2 component of PRC1-AUTS2 neutralizes PRC1 repressive activity, whereas AUTS2-mediated recruitment of P300 leads to gene activation. Chromatin immunoprecipitation followed by sequencing (ChIP-seq) demonstrated that AUTS2 regulates neuronal gene expression through promoter association. Conditional targeting of Auts2 in the mouse central nervous system (CNS) leads to various developmental defects. These findings reveal a natural means of subverting PRC1 activity, linking key epigenetic modulators with neuronal functions and diseases.
Figures
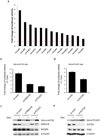
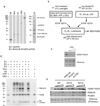
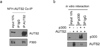


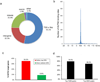
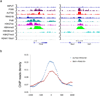
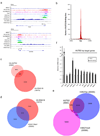
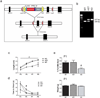
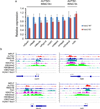






References
-
- Muller J, Verrijzer P. Biochemical mechanisms of gene regulation by polycomb group protein complexes. Current opinion in genetics & development. 2009;19:150–158. - PubMed
-
- Morey L, Helin K. Polycomb group protein-mediated repression of transcription. Trends Biochem Sci. 2010;35:323–332. - PubMed
-
- Schuettengruber B, Cavalli G. Recruitment of polycomb group complexes and their role in the dynamic regulation of cell fate choice. Development. 2009;136:3531–3542. - PubMed
References (For Methods)
-
- Vaquero A, et al. Human SirT1 interacts with histone H1 and promotes formation of facultative heterochromatin. Mol Cell. 2004;16:93–105. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- P30 CA016087/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- 5T32CA160002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- DP2 MH100012/MH/NIMH NIH HHS/United States
- GM-64844/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- 1F32GM105275/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM064844/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- Howard Hughes Medical Institute/United States
- F32AA022842/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- 1DP2MH100012-01/DP/NCCDPHP CDC HHS/United States
- T32 CA160002/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- F32 AA022842/AA/NIAAA NIH HHS/United States
- F32 GM105275/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

