DNA-PKcs-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation Drives Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastasis
- PMID: 26175416
- PMCID: PMC4531387
- DOI: 10.1016/j.ccell.2015.06.004
DNA-PKcs-Mediated Transcriptional Regulation Drives Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastasis
Abstract
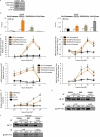
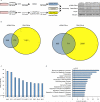
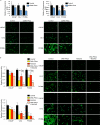
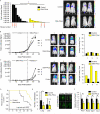
Emerging evidence demonstrates that the DNA repair kinase DNA-PKcs exerts divergent roles in transcriptional regulation of unsolved consequence. Here, in vitro and in vivo interrogation demonstrate that DNA-PKcs functions as a selective modulator of transcriptional networks that induce cell migration, invasion, and metastasis. Accordingly, suppression of DNA-PKcs inhibits tumor metastases. Clinical assessment revealed that DNA-PKcs is significantly elevated in advanced disease and independently predicts for metastases, recurrence, and reduced overall survival. Further investigation demonstrated that DNA-PKcs in advanced tumors is highly activated, independent of DNA damage indicators. Combined, these findings reveal unexpected DNA-PKcs functions, identify DNA-PKcs as a potent driver of tumor progression and metastases, and nominate DNA-PKcs as a therapeutic target for advanced malignancies.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



References
-
- Al-Ubaidi FL, Schultz N, Loseva O, Egevad L, Granfors T, Helleday T. Castration therapy results in decreased Ku70 levels in prostate cancer. Clin Cancer Res. 2013;19:1547–56. - PubMed
-
- Aytes A, Mitrofanova A, Kinkade CW, Lefebvre C, Lei M, Phelan V, LeKaye HC, Koutcher JA, Cardiff RD, Califano A, et al. ETV4 promotes metastasis in response to activation of PI3-kinase and Ras signaling in a mouse model of advanced prostate cancer. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2013;110:E3506–15. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
- CA173481/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA183929/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25 CA098010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA176401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA173481/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA168585/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- UL1 TR000124/TR/NCATS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA159945/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R25T CA098010/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- CA159945/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- GM089778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA176401/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P01 CA168585/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 GM089778/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
- P30 CA056036/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- R01 CA183929/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

