JMJD1C is required for the survival of acute myeloid leukemia by functioning as a coactivator for key transcription factors
- PMID: 26494788
- PMCID: PMC4617977
- DOI: 10.1101/gad.267278.115
JMJD1C is required for the survival of acute myeloid leukemia by functioning as a coactivator for key transcription factors
Abstract
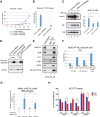
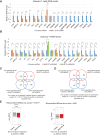
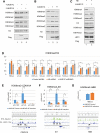
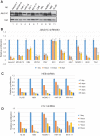
RUNX1-RUNX1T1 (formerly AML1-ETO), a transcription factor generated by the t(8;21) translocation in acute myeloid leukemia (AML), dictates a leukemic program by increasing self-renewal and inhibiting differentiation. Here we demonstrate that the histone demethylase JMJD1C functions as a coactivator for RUNX1-RUNX1T1 and is required for its transcriptional program. JMJD1C is directly recruited by RUNX1-RUNX1T1 to its target genes and regulates their expression by maintaining low H3K9 dimethyl (H3K9me2) levels. Analyses in JMJD1C knockout mice also establish a JMJD1C requirement for RUNX1-RUNX1T1's ability to increase proliferation. We also show a critical role for JMJD1C in the survival of multiple human AML cell lines, suggesting that it is required for leukemic programs in different AML cell types through its association with key transcription factors.
Keywords: AML1-ETO; HEB; LYL1; acute myeloid leukemia; histone demethylase; transcription regulation.
© 2015 Chen et al.; Published by Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press.
Figures



References
-
- Ben-Ami O, Friedman D, Leshkowitz D, Goldenberg D, Orlovsky K, Pencovich N, Lotem J, Tanay A, Groner Y. 2013. Addiction of t(8;21) and inv(16) acute myeloid leukemia to native RUNX1. Cell Rep 4: 1131–1143. - PubMed
-
- Cabezas-Wallscheid N, Eichwald V, de Graaf J, Lower M, Lehr HA, Kreft A, Eshkind L, Hildebrandt A, Abassi Y, Heck R, et al. 2013. Instruction of haematopoietic lineage choices, evolution of transcriptional landscapes and cancer stem cell hierarchies derived from an AML1-ETO mouse model. EMBO Mol Med 5: 1804–1820. - PMC - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous
