Convergence of developmental and oncogenic signaling pathways at transcriptional super-enhancers
- PMID: 25801169
- PMCID: PMC4402134
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.02.014
Convergence of developmental and oncogenic signaling pathways at transcriptional super-enhancers
Abstract
Super-enhancers and stretch enhancers (SEs) drive expression of genes that play prominent roles in normal and disease cells, but the functional importance of these clustered enhancer elements is poorly understood, so it is not clear why genes key to cell identity have evolved regulation by such elements. Here, we show that SEs consist of functional constituent units that concentrate multiple developmental signaling pathways at key pluripotency genes in embryonic stem cells and confer enhanced responsiveness to signaling of their associated genes. Cancer cells frequently acquire SEs at genes that promote tumorigenesis, and we show that these genes are especially sensitive to perturbation of oncogenic signaling pathways. Super-enhancers thus provide a platform for signaling pathways to regulate genes that control cell identity during development and tumorigenesis.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures
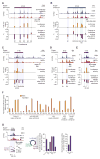
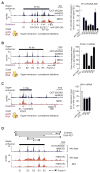
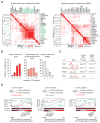
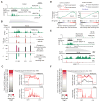
Comment in
-
Super-enhancers facilitate gene regulation by signaling pathways.Cancer Discov. 2015 May;5(5):OF11. doi: 10.1158/2159-8290.CD-RW2015-056. Epub 2015 Mar 26. Cancer Discov. 2015. PMID: 25813350 No abstract available.
References
-
- Chen X, Xu H, Yuan P, Fang F, Huss M, Vega VB, Wong E, Orlov YL, Zhang W, Jiang J, et al. Integration of external signaling pathways with the core transcriptional network in embryonic stem cells. Cell. 2008;133:1106–1117. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

