RFX transcription factors are essential for hearing in mice
- PMID: 26469318
- PMCID: PMC4634137
- DOI: 10.1038/ncomms9549
RFX transcription factors are essential for hearing in mice
Abstract
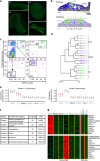
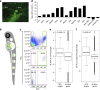
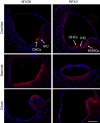
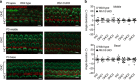
Sensorineural hearing loss is a common and currently irreversible disorder, because mammalian hair cells (HCs) do not regenerate and current stem cell and gene delivery protocols result only in immature HC-like cells. Importantly, although the transcriptional regulators of embryonic HC development have been described, little is known about the postnatal regulators of maturating HCs. Here we apply a cell type-specific functional genomic analysis to the transcriptomes of auditory and vestibular sensory epithelia from early postnatal mice. We identify RFX transcription factors as essential and evolutionarily conserved regulators of the HC-specific transcriptomes, and detect Rfx1,2,3,5 and 7 in the developing HCs. To understand the role of RFX in hearing, we generate Rfx1/3 conditional knockout mice. We show that these mice are deaf secondary to rapid loss of initially well-formed outer HCs. These data identify an essential role for RFX in hearing and survival of the terminally differentiating outer HCs.
Conflict of interest statement
Scott Strome is a Cofounder and Major stockholder in Gliknik Inc., a biotechnology company. He also receives royalties for intellectual property, related to B7-H1 (PD-L1), licensed by the Mayo Clinic College of Medicine to third parties. The remaining authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures



References
-
- Morton N. E. Genetic epidemiology of hearing impairment. Ann. NY Acad. Sci. 630, 16–31 (1991). - PubMed
-
- Ruben R. J. Development of the inner ear of the mouse: a radioautographic study of terminal mitoses. Acta Otolaryngol. 220, (Suppl): 1–44 (1967). - PubMed
-
- Bermingham N. A. et al.. Math1: an essential gene for the generation of inner ear hair cells. Science 284, 1837–1841 (1999). - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
- S10 RR024548/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC014658/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01DK102001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC013817/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- U01 DC013817/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01DC03544/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- P30 DK072488/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- K01 DK092402/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DC014658/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DK102001/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
- R01DC013817/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- R01 DC003544/DC/NIDCD NIH HHS/United States
- K01DK092402/DK/NIDDK NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

