De Novo Reconstruction of Adipose Tissue Transcriptomes Reveals Long Non-coding RNA Regulators of Brown Adipocyte Development
- PMID: 25921091
- PMCID: PMC4429916
- DOI: 10.1016/j.cmet.2015.04.003
De Novo Reconstruction of Adipose Tissue Transcriptomes Reveals Long Non-coding RNA Regulators of Brown Adipocyte Development
Erratum in
- Cell Metab. 2015 Jun 2;21(6):918
Abstract
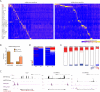
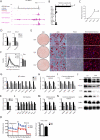
Brown adipose tissue (BAT) protects against obesity by promoting energy expenditure via uncoupled respiration. To uncover BAT-specific long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs), we used RNA-seq to reconstruct de novo transcriptomes of mouse brown, inguinal white, and epididymal white fat and identified ∼1,500 lncRNAs, including 127 BAT-restricted loci induced during differentiation and often targeted by key regulators PPARγ, C/EBPα, and C/EBPβ. One of them, lnc-BATE1, is required for establishment and maintenance of BAT identity and thermogenic capacity. lnc-BATE1 inhibition impairs concurrent activation of brown fat and repression of white fat genes and is partially rescued by exogenous lnc-BATE1 with mutated siRNA-targeting sites, demonstrating a function in trans. We show that lnc-BATE1 binds heterogeneous nuclear ribonucleoprotein U and that both are required for brown adipogenesis. Our work provides an annotated catalog for the study of fat depot-selective lncRNAs and establishes lnc-BATE1 as a regulator of BAT development and physiology.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
