The Menu of Features that Define Primary MicroRNAs and Enable De Novo Design of MicroRNA Genes
- PMID: 26412306
- PMCID: PMC4613790
- DOI: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.08.015
The Menu of Features that Define Primary MicroRNAs and Enable De Novo Design of MicroRNA Genes
Abstract
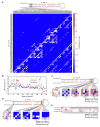
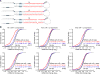
MicroRNAs (miRNAs) are small regulatory RNAs processed from stem-loop regions of primary transcripts (pri-miRNAs), with the choice of stem loops for initial processing largely determining what becomes a miRNA. To identify sequence and structural features influencing this choice, we determined cleavage efficiencies of >50,000 variants of three human pri-miRNAs, focusing on the regions intractable to previous high-throughput analyses. Our analyses revealed a mismatched motif in the basal stem region, a preference for maintaining or improving base pairing throughout the remainder of the stem, and a narrow stem-length preference of 35 ± 1 base pairs. Incorporating these features with previously identified features, including three primary-sequence motifs, yielded a unifying model defining mammalian pri-miRNAs in which motifs help orient processing and increase efficiency, with the presence of more motifs compensating for structural defects. This model enables generation of artificial pri-miRNAs, designed de novo, without reference to any natural sequence yet processed more efficiently than natural pri-miRNAs.
Copyright © 2015 Elsevier Inc. All rights reserved.
Figures



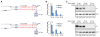

Comment in
-
The Long, the Short, and the Unstructured: A Unifying Model of miRNA Biogenesis.Mol Cell. 2015 Oct 1;60(1):4-6. doi: 10.1016/j.molcel.2015.09.014. Mol Cell. 2015. PMID: 26431024
References
-
- Grishok A, Pasquinelli AE, Conte D, Li N, Parrish S, Ha I, Baillie DL, Fire A, Ruvkun G, Mello CC. Genes and mechanisms related to RNA interference regulate expression of the small temporal RNAs that control C. elegans developmental timing. Cell. 2001;106:23–34. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G, McLachlan J, Pasquinelli AE, Balint E, Tuschl T, Zamore PD. A cellular function for the RNA-interference enzyme Dicer in the maturation of the let-7 small temporal RNA. Science. 2001;293:834–838. - PubMed
-
- Hutvagner G, Zamore PD. A microRNA in a multiple-turnover RNAi enzyme complex. Science. 2002;297:2056–2060. - PubMed
-
- Zeng Y, Wagner EJ, Cullen BR. Both natural and designed micro RNAs can inhibit the expression of cognate mRNAs when expressed in human cells. Mol Cell. 2002;9:1327–1333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

