Multilevel interactions between ethylene and auxin in Arabidopsis roots
- PMID: 17630276
- PMCID: PMC1955696
- DOI: 10.1105/tpc.107.052068
Multilevel interactions between ethylene and auxin in Arabidopsis roots
Abstract
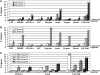
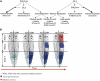
Hormones play a central role in the coordination of internal developmental processes with environmental signals. Herein, a combination of physiological, genetic, cellular, and whole-genome expression profiling approaches has been employed to investigate the mechanisms of interaction between two key plant hormones: ethylene and auxin. Quantification of the morphological effects of ethylene and auxin in a variety of mutant backgrounds indicates that auxin biosynthesis, transport, signaling, and response are required for the ethylene-induced growth inhibition in roots but not in hypocotyls of dark-grown seedlings. Analysis of the activation of early auxin and ethylene responses at the cellular level, as well as of global changes in gene expression in the wild type versus auxin and ethylene mutants, suggests a simple mechanistic model for the interaction between these two hormones in roots, according to which ethylene and auxin can reciprocally regulate each other's biosyntheses, influence each other's response pathways, and/or act independently on the same target genes. This model not only implies existence of several levels of interaction but also provides a likely explanation for the strong ethylene response defects observed in auxin mutants.
Figures

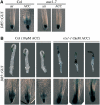
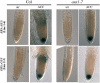
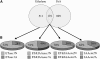
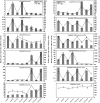
References
-
- Abel, S., Nguyen, M.D., Chow, W., and Theologis, A. (1995). ACS4, a primary indole acetic acid-responsive gene encoding 1-aminocyclopropane-1-carboxylate synthase in Arabidopsis thaliana. Structural characterization, expression in Escherichia coli, and expression characteristics in response to auxin. J. Biol. Chem. 270 19093–19099. Erratum. J. Biol. Chem. 270: 26020. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., and Ecker, J.R. (2001). The ethylene pathway: A paradigm for plant hormone signaling and interaction. Sci. STKE 2001 RE1. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., and Stepanova, A.N. (2004). The ethylene signaling pathway. Science 306 1513–1515. - PubMed
-
- Alonso, J.M., et al. (2003. b). Genome-wide insertional mutagenesis of Arabidopsis thaliana. Science 301 653–657. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

