Single-cell transcriptomics reveals receptor transformations during olfactory neurogenesis
- PMID: 26541607
- PMCID: PMC5642900
- DOI: 10.1126/science.aad2456
Single-cell transcriptomics reveals receptor transformations during olfactory neurogenesis
Abstract
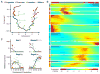
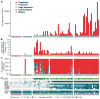
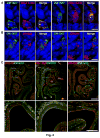
The sense of smell allows chemicals to be perceived as diverse scents. We used single-neuron RNA sequencing to explore the developmental mechanisms that shape this ability as nasal olfactory neurons mature in mice. Most mature neurons expressed only one of the ~1000 odorant receptor genes (Olfrs) available, and at a high level. However, many immature neurons expressed low levels of multiple Olfrs. Coexpressed Olfrs localized to overlapping zones of the nasal epithelium, suggesting regional biases, but not to single genomic loci. A single immature neuron could express Olfrs from up to seven different chromosomes. The mature state in which expression of Olfr genes is restricted to one per neuron emerges over a developmental progression that appears to be independent of neuronal activity involving sensory transduction molecules.
Copyright © 2015, American Association for the Advancement of Science.
Figures

References
-
- Buck L, Axel R. Cell. 1991;65:175. - PubMed
-
- Buck LB, Bargmann C. In: Principles of Neuroscience. Kandel E, Schwartz J, Jessell T, Siegelbaum S, Hudspeth AJ, editors. McGraw-Hill; New York: 2012. pp. 712–742.
-
- Zhang X, Firestein S. Nat Neurosci. 2002;5:124. - PubMed
-
- Niimura Y, Nei M. Gene. 2005;346:13. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

