Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated gene expression by a sequence-specific DNA-binding polyamide
- PMID: 17566103
- PMCID: PMC1965528
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0704217104
Suppression of androgen receptor-mediated gene expression by a sequence-specific DNA-binding polyamide
Abstract
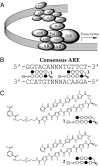
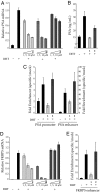
Androgen receptor (AR) is essential for the growth and progression of prostate cancer in both hormone-sensitive and hormone-refractory disease. A DNA-binding polyamide that targets the consensus androgen response element binds the prostate-specific antigen (PSA) promoter androgen response element, inhibits androgen-induced expression of PSA and several other AR-regulated genes in cultured prostate cancer cells, and reduces AR occupancy at the PSA promoter and enhancer. Down-regulation of PSA by this polyamide was comparable to that produced by the synthetic antiandrogen bicalutamide (Casodex) at the same concentration. Genome-wide expression analysis reveals that a similar number of transcripts are affected by treatment with the polyamide and with bicalutamide. Direct inhibition of the AR-DNA interface by sequence-specific DNA binding small molecules could offer an alternative approach to antagonizing AR activity.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures


References
-
- Tsai MJ, Omalley BW. Annu Rev Biochem. 1994;63:451–486. - PubMed
-
- Tyagi RK, Lavrovsky Y, Ahn SC, Song CS, Chatterjee B, Roy AK. Mol Endocrinol. 2000;14:1162–1174. - PubMed
-
- Roche PJ, Hoare SA, Parker MG. Mol Endocrinol. 1992;6:2229–2235. - PubMed
-
- Cleutjens KB, van der Korput HA, van Eekelen CC, van Rooij HC, Faber PW, Trapman J. Mol Endocrinol. 1997;11:148–161. - PubMed
-
- Cleutjens KB, van Eekelen CC, van der Korput HA, Brinkmann AO, Trapman J. J Biol Chem. 1996;271:6379–6388. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

