The role of the NMD factor UPF3B in olfactory sensory neurons
- PMID: 32773035
- PMCID: PMC7452722
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.57525
The role of the NMD factor UPF3B in olfactory sensory neurons
Abstract
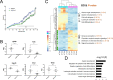
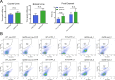
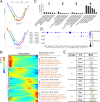
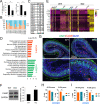
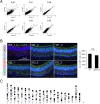
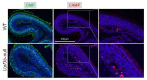
The UPF3B-dependent branch of the nonsense-mediated RNA decay (NMD) pathway is critical for human cognition. Here, we examined the role of UPF3B in the olfactory system. Single-cell RNA-sequencing (scRNA-seq) analysis demonstrated considerable heterogeneity of olfactory sensory neuron (OSN) cell populations in wild-type (WT) mice, and revealed that UPF3B loss influences specific subsets of these cell populations. UPF3B also regulates the expression of a large cadre of antimicrobial genes in OSNs, and promotes the selection of specific olfactory receptor (Olfr) genes for expression in mature OSNs (mOSNs). RNA-seq and Ribotag analyses identified classes of mRNAs expressed and translated at different levels in WT and Upf3b-null mOSNs. Integrating multiple computational approaches, UPF3B-dependent NMD target transcripts that are candidates to mediate the functions of NMD in mOSNs were identified in vivo. Together, our data provides a valuable resource for the olfactory field and insights into the roles of NMD in vivo.
Keywords: NMD; Upf3b; anti-microbial genes; developmental biology; mouse; neuroscience; olfactory receptor; olfactory sensory neuron; scRNA-seq.
© 2020, Tan et al.
Conflict of interest statement
KT, SJ, BL, JD, ES, LZ, SC, AS, SP, RG, KZ, HC, MW No competing interests declared
Figures






References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

