Targeting LINC00152 activates cAMP/Ca2+/ferroptosis axis and overcomes tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer
- PMID: 38879508
- PMCID: PMC11180193
- DOI: 10.1038/s41419-024-06814-3
Targeting LINC00152 activates cAMP/Ca2+/ferroptosis axis and overcomes tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer
Abstract
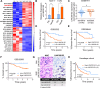
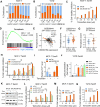
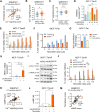
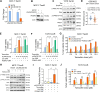
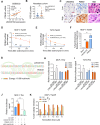
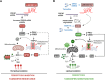
Tamoxifen has been the mainstay therapy to treat early, locally advanced, and metastatic estrogen receptor-positive (ER + ) breast cancer, constituting around 75% of all cases. However, the emergence of resistance is common, necessitating the identification of novel therapeutic targets. Here, we demonstrated that long-noncoding RNA LINC00152 confers tamoxifen resistance by blocking tamoxifen-induced ferroptosis, an iron-mediated cell death. Mechanistically, inhibiting LINC00152 reduces the mRNA stability of phosphodiesterase 4D (PDE4D), leading to activation of the cAMP/PKA/CREB axis and increased expression of the TRPC1 Ca2+ channel. This causes cytosolic Ca2+ overload and generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) that is, on the one hand, accompanied by downregulation of FTH1, a member of the iron sequestration unit, thus increasing intracellular Fe2+ levels; and on the other hand, inhibition of the peroxidase activity upon reduced GPX4 and xCT levels, in part by cAMP/CREB. These ultimately restore tamoxifen-dependent lipid peroxidation and ferroptotic cell death which are reversed upon chelating Ca2+ or overexpressing GPX4 or xCT. Overexpressing PDE4D reverses LINC00152 inhibition-mediated tamoxifen sensitization by de-activating the cAMP/Ca2+/ferroptosis axis. Importantly, high LINC00152 expression is significantly correlated with high PDE4D/low ferroptosis and worse survival in multiple cohorts of tamoxifen- or tamoxifen-containing endocrine therapy-treated ER+ breast cancer patients. Overall, we identified LINC00152 inhibition as a novel mechanism of tamoxifen sensitization via restoring tamoxifen-dependent ferroptosis upon destabilizing PDE4D, increasing cAMP and Ca2+ levels, thus leading to ROS generation and lipid peroxidation. Our findings reveal LINC00152 and its effectors as actionable therapeutic targets to improve clinical outcome in refractory ER+ breast cancer.
© 2024. The Author(s).
Conflict of interest statement
O.S. is the co-founder of OncoCube Therapeutics LLC, the founder and president of LoxiGen, Inc., and the scientific advisory board member of A2A Pharmaceuticals. The other authors declare no potential competing interests.
Figures

Update of
-
Targeting LINC00152 activates cAMP/Ca2+/ferroptosis axis and overcomes tamoxifen resistance in ER+ breast cancer.bioRxiv [Preprint]. 2023 Nov 5:2023.11.05.565697. doi: 10.1101/2023.11.05.565697. bioRxiv. 2023. Update in: Cell Death Dis. 2024 Jun 15;15(6):418. doi: 10.1038/s41419-024-06814-3. PMID: 38496603 Free PMC article. Updated. Preprint.
References
-
- Early Breast Cancer Trialists’ Collaborative G. Davies C, Godwin J, Gray R, Clarke M, Cutter D, et al. Relevance of breast cancer hormone receptors and other factors to the efficacy of adjuvant tamoxifen: patient-level meta-analysis of randomised trials. Lancet. 2011;378:771–84. doi: 10.1016/S0140-6736(11)60993-8. - DOI - PMC - PubMed
-
- Ekholm M, Bendahl PO, Fernö M, Nordenskjöld B, Stål O, Rydén L. Two Years of Adjuvant Tamoxifen Provides a Survival Benefit Compared With No Systemic Treatment in Premenopausal Patients With Primary Breast Cancer: Long-Term Follow-Up (> 25 years) of the Phase III SBII:2pre Trial. J Clin Oncol 34(19):2232-2238. 10.1200/JCO.2015.65.6272. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- BioProject/PRJNA1040324
- BioProject/PRJNA1036119
Grants and funding
- GTDR17500160/Susan G. Komen (Susan G. Komen Breast Cancer Foundation)
- C06 RR015455/RR/NCRR NIH HHS/United States
- R01CA251374/Foundation for the National Institutes of Health (Foundation for the National Institutes of Health, Inc.)
- R01 CA267101/CA/NCI NIH HHS/United States
- P30 GM103339/GM/NIGMS NIH HHS/United States
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

