PRD-2 directly regulates casein kinase I and counteracts nonsense-mediated decay in the Neurospora circadian clock
- PMID: 33295874
- PMCID: PMC7746235
- DOI: 10.7554/eLife.64007
PRD-2 directly regulates casein kinase I and counteracts nonsense-mediated decay in the Neurospora circadian clock
Abstract
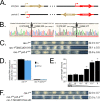
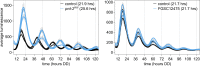
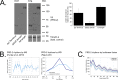
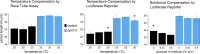
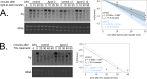
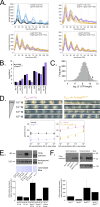
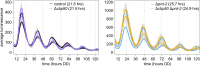
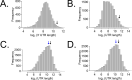
Circadian clocks in fungi and animals are driven by a functionally conserved transcription-translation feedback loop. In Neurospora crassa, negative feedback is executed by a complex of Frequency (FRQ), FRQ-interacting RNA helicase (FRH), and casein kinase I (CKI), which inhibits the activity of the clock's positive arm, the White Collar Complex (WCC). Here, we show that the prd-2 (period-2) gene, whose mutation is characterized by recessive inheritance of a long 26 hr period phenotype, encodes an RNA-binding protein that stabilizes the ck-1a transcript, resulting in CKI protein levels sufficient for normal rhythmicity. Moreover, by examining the molecular basis for the short circadian period of upf-1prd-6 mutants, we uncovered a strong influence of the Nonsense Mediated Decay pathway on CKI levels. The finding that circadian period defects in two classically derived Neurospora clock mutants each arise from disruption of ck-1a regulation is consistent with circadian period being exquisitely sensitive to levels of casein kinase I.
Keywords: Casein Kinase I; N. crassa; RNA-binding protein; SUZ domain; circadian clock; genetics; genomics; neurospora; nonsense mediated decay; prd-2, upf1 / prd-6.
© 2020, Kelliher et al.
Conflict of interest statement
CK, RL, QX, CB, JL, JD No competing interests declared
Figures




References
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials
Miscellaneous

