Evolutionarily conserved gene family important for fat storage
- PMID: 18160536
- PMCID: PMC2224239
- DOI: 10.1073/pnas.0708579105
Evolutionarily conserved gene family important for fat storage
Abstract
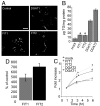
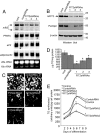
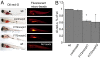
The ability to store fat in the form of cytoplasmic triglyceride droplets is conserved from Saccharomyces cerevisiae to humans. Although much is known regarding the composition and catabolism of lipid droplets, the molecular components necessary for the biogenesis of lipid droplets have remained obscure. Here we report the characterization of a conserved gene family important for lipid droplet formation named fat-inducing transcript (FIT). FIT1 and FIT2 are endoplasmic reticulum resident membrane proteins that induce lipid droplet accumulation in cell culture and when expressed in mouse liver. shRNA silencing of FIT2 in 3T3-LI adipocytes prevents accumulation of lipid droplets, and depletion of FIT2 in zebrafish blocks diet-induced accumulation of lipid droplets in the intestine and liver, highlighting an important role for FIT2 in lipid droplet formation in vivo. Together these studies identify and characterize a conserved gene family that is important in the fundamental process of storing fat.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
Figures



References
-
- Martin S, Parton RG. Nat Rev Mol Cell Biol. 2006;7:373–378. - PubMed
-
- Spiegelman BM, Flier JS. Cell. 2001;104:531–543. - PubMed
-
- Brasaemle DL, Dolios G, Shapiro L, Wang R. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:46835–46842. - PubMed
-
- Liu P, Ying Y, Zhao Y, Mundy DI, Zhu M, Anderson RG. J Biol Chem. 2004;279:3787–3792. - PubMed
-
- Beller M, Riedel D, Jansch L, Dieterich G, Wehland J, Jackle H, Kuhnlein RP. Mol Cell Proteomics. 2006;5:1082–1094. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

