The Drosophila hairpin RNA pathway generates endogenous short interfering RNAs
- PMID: 18463630
- PMCID: PMC2735555
- DOI: 10.1038/nature07015
The Drosophila hairpin RNA pathway generates endogenous short interfering RNAs
Abstract
In contrast to microRNAs and Piwi-associated RNAs, short interfering RNAs (siRNAs) are seemingly dispensable for host-directed gene regulation in Drosophila. This notion is based on the fact that mutants lacking the core siRNA-generating enzyme Dicer-2 or the predominant siRNA effector Argonaute 2 are viable, fertile and of relatively normal morphology. Moreover, endogenous Drosophila siRNAs have not yet been identified. Here we report that siRNAs derived from long hairpin RNA genes (hpRNAs) programme Slicer complexes that can repress endogenous target transcripts. The Drosophila hpRNA pathway is a hybrid mechanism that combines canonical RNA interference factors (Dicer-2, Hen1 (known as CG12367) and Argonaute 2) with a canonical microRNA factor (Loquacious) to generate approximately 21-nucleotide siRNAs. These novel regulatory RNAs reveal unexpected complexity in the sorting of small RNAs, and open a window onto the biological usage of endogenous RNA interference in Drosophila.
Figures
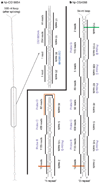
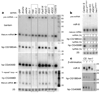
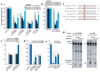
Comment in
-
Genomics: protein fossils live on as RNA.Nature. 2008 Jun 5;453(7196):729-31. doi: 10.1038/453729a. Nature. 2008. PMID: 18528383 No abstract available.
References
-
- Lee YS, et al. Distinct roles for Drosophila Dicer-1 and Dicer-2 in the siRNA/miRNA silencing pathways. Cell. 2004;117:69–81. - PubMed
-
- Kennerdell JR, Carthew RW. Heritable gene silencing in Drosophila using double-stranded RNA. Nature Biotechnol. 2000;18:896–898. - PubMed
-
- Rice P, Longden I, Bleasby A. EMBOSS: the European Molecular Biology Open Software Suite. Trends Genet. 2000;16:276–277. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

