Genetic and phenotypic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum biovar 2 strains obtained from Dutch waterways
- PMID: 19960250
- PMCID: PMC2797627
- DOI: 10.1007/s10482-009-9400-1
Genetic and phenotypic diversity of Ralstonia solanacearum biovar 2 strains obtained from Dutch waterways
Abstract
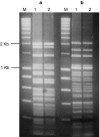
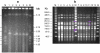
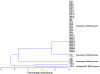
A novel set of Ralstonia solanacearum biovar 2 isolates was obtained, at several sampling occasions, from Dutch waterways, sediment and bittersweet plants and their genetic and phenotypic diversity was investigated. As reference strains, two previously-described strains obtained from diseased potato plants, denoted 1609 (The Netherlands) and 715 (Bangladesh), were included in the analyses. All novel isolates showed BOX and GTG5 PCR based genomic profiles similar to those of the reference strains. Also, PCR-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis of the phcA and hrp genomic regions, as well as sequence analysis of six selected genomic loci, revealed great homogeneity across the strains. In contrast, pulsed field gel electrophoresis of restricted genomic DNA revealed the distribution of all strains across four groups, denoted pulsotypes A through D (pulsotypes C and D had one representative each). Moreover, pulsotype B, consisting of five strains, could be separated from the other pulsotypes by a divergent genomic fingerprint when hybridized to a probe specific for insertion element ISRso3. Representatives of pulsotypes A, B and C were selected for growth and metabolic studies. They showed similar growth rates when grown aerobically in liquid media. Assessment of their metabolic capacity using BIOLOG GN-2 revealed a reduced utilization of compounds as compared to the reference strains, with some variation between strains.
Figures

References
-
- Arlat M, Boucher C. Identification of a Dsp DNA region controlling aggressiveness of Pseudomonas solanacearum. Mol Plant Microbe Interact. 1991;4:211–213.
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Research Materials

