Complete genome sequences of avian paramyxovirus serotype 6 prototype strain Hong Kong and a recent novel strain from Italy: evidence for the existence of subgroups within the serotype
- PMID: 20206652
- PMCID: PMC2859990
- DOI: 10.1016/j.virusres.2010.02.015
Complete genome sequences of avian paramyxovirus serotype 6 prototype strain Hong Kong and a recent novel strain from Italy: evidence for the existence of subgroups within the serotype
Abstract
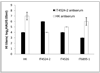
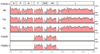
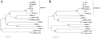
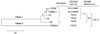
Complete genome sequences were determined for two strains of avian paramyxovirus serotype 6 (APMV-6): the prototype Hong Kong (HK) strain and a more recent isolate from Italy (IT4524-2). The genome length of strain HK is 16236 nucleotide (nt), which is the same as for the other two APMV-6 strains (FE and TW) that have been reported to date, whereas that of strain IT4524-2 is 16230 nt. The length difference in strain IT4524-2 is due to a 6-nt deletion in the downstream untranslated region of the F gene. All of these viruses follow the "rule of six". Each genome consists of seven genes in the order of 3'N-P-M-F-SH-HN-L5', which differs from other APMV serotypes in containing an additional gene encoding the small hydrophobic (SH) protein. Sequence comparisons revealed that strain IT4524-2 shares an unexpectedly low level of genome nt sequence identity (70%) and aggregate predicted amino acid (aa) sequence identity (79%) with other three strains, which in contrast are more closely related to each other with nt sequence 94-98% nt identity and 90-100% aggregate aa identity. Sequence analysis of the F-SH-HN genome region of two other recent Italian isolates showed that they fall in the HK/FE/TW group. The predicted signal peptide of IT4524-2 F protein lacks the N-terminal first 10 aa that are present in the other five strains. Also, the F protein cleavage site of strain IT4524-2, REPR downward arrow L, has two dibasic aa (arginine, R) compared to the monobasic F protein cleavage site of PEPR downward arrow L in the other strains. Reciprocal cross-hemagglutination inhibition (HI) assays using post-infection chicken sera indicated that strain IT4524-2 is antigenically related to the other APMV-6 strains, but with 4- to 8-fold lower HI tiers for the test sera between strain IT4524-2 and the other APMV-6 strains. Taken together, our results indicated that the APMV-6 strains represents a single serotype with two subgroups that differ substantially based on nt and aa sequences and can be distinguished by HI assay.
(c) 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures





References
-
- Alexander DJ. Newcastle disease and other avian Paramyxoviridae infections. In: Calnek BW, editor. Diseases of Poultry. Ames: Iowa State University Press; 1997. pp. 541–569.
-
- Alexander DJ. Avian Paramyxoviruses 2–9. In: Saif YM, editor. Diseases of poultry. 11th edn. Ames: Iowa State University Press; 2003. pp. 88–92.
-
- Alexander DJ, Collins MS. Pathogenecity of PMV-3/Parakeet/Netherland/449 /75 for chickens. Avian Pathol. 1982;11:179–185. - PubMed
-
- Bendtsen JD, Nielsen H, von Heijne G, Brunak S. Improved prediction of signal peptides: Signal 3.0. J Mol Biol. 2004;340:783–795. - PubMed
-
- Biacchesi S, Skiadopoulos MH, Boivin G, Hanson CT, Murphy BR, Collins PL, Buchholz UJ. Genetic diversity between human metapneumovirus subgroups. Virology. 2003;315:1–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Research Materials

