A flow cytometry-based strategy to identify and express IgM from VH1-69+ clonal peripheral B cells
- PMID: 20875420
- PMCID: PMC3003765
- DOI: 10.1016/j.jim.2010.09.022
A flow cytometry-based strategy to identify and express IgM from VH1-69+ clonal peripheral B cells
Abstract
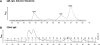
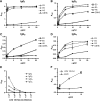
Pathologic rheumatoid factor (RF) levels are hallmarks of several human diseases. Production of monoclonal RF in vitro is essential for studies of the antigenic specificities of RF, as well as for a dissection of the mechanisms of aberrant RF+ B cell activation. We have expanded upon previous methods to develop a flow cytometry-based method to efficiently clone monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) from humans with expansions of RF-like, immunoglobulin heavy chain variable region (IgVH) 1-69 gene segment-containing B cells. The cloned variable regions are expressed as IgM and produced during culture at concentrations between 5 and 20 μg/ml. Using this system, we show that clonal Igs from patients with HCV-related mixed cryoglobulinemia, when expressed as IgM, have RF activity. We anticipate that this system will be useful for the cloning and expression of mAbs partially encoded by VH1-69 and for determination of the reactivity patterns of polyspecific, low-affinity IgMs of human pathogenic importance.
Copyright © 2010 Elsevier B.V. All rights reserved.
Figures

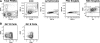

References
-
- National Center for Biotechnology Information GenBank. [Accessed October 1, 2009]. http://ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/Genbank.
-
- Bonagura VR, Agostino N, Borretzen M, Thompson KM, Natvig JB, Morrison SL. Mapping IgG epitopes bound by rheumatoid factors from immunized controls identifies disease-specific rheumatoid factors produced by patients with rheumatoid arthritis. J Immunol. 1998;160:2496–505. - PubMed
-
- Carbonari M, Caprini E, Tedesco T, Mazzetta F, Tocco V, Casato M, Russo G, Fiorilli M. Hepatitis C virus drives the unconstrained monoclonal expansion of VH1-69-expressing memory B cells in type II cryoglobulinemia: a model of infection-driven lymphomagenesis. J Immunol. 2005;174:6532–9. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Miscellaneous

