A comparative transcriptomic analysis of astrocytes differentiation from human neural progenitor cells
- PMID: 27564458
- PMCID: PMC5118072
- DOI: 10.1111/ejn.13382
A comparative transcriptomic analysis of astrocytes differentiation from human neural progenitor cells
Abstract
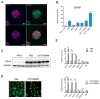
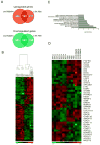
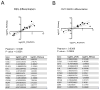
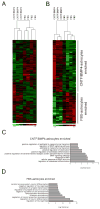
Astrocytes are a morphologically and functionally heterogeneous population of cells that play critical roles in neurodevelopment and in the regulation of central nervous system homeostasis. Studies of human astrocytes have been hampered by the lack of specific molecular markers and by the difficulties associated with purifying and culturing astrocytes from adult human brains. Human neural progenitor cells (NPCs) with self-renewal and multipotent properties represent an appealing model system to gain insight into the developmental genetics and function of human astrocytes, but a comprehensive molecular characterization that confirms the validity of this cellular system is still missing. Here we used an unbiased transcriptomic analysis to characterize in vitro culture of human NPCs and to define the gene expression programs activated during the differentiation of these cells into astrocytes using FBS or the combination of CNTF and BMP4. Our results demonstrate that in vitro cultures of human NPCs isolated during the gliogenic phase of neurodevelopment mainly consist of radial glial cells (RGCs) and glia-restricted progenitor cells. In these cells the combination of CNTF and BMP4 activates the JAK/STAT and SMAD signaling cascades, leading to the inhibition of oligodendrocytes lineage commitment and activation of astrocytes differentiation. On the other hand, FBS-derived astrocytes have properties of reactive astrocytes. Our work suggests that in vitro culture of human NPCs represents a valuable cellular system to study human disorders characterized by impairment of astrocytes development and function. Our datasets represent an important resource for researchers studying human astrocytes development and might set the basis for the discovery of novel human-specific astrocyte markers.
Keywords: gliogenesis; human astrocytes; neural progenitor cells; neurodevelopment; radial glial cells; transcriptomic.
© 2016 The Authors. European Journal of Neuroscience published by Federation of European Neuroscience Societies and John Wiley & Sons Ltd.
Conflict of interest statement
All authors indicate no potential conflicts of interest.
Figures
References
-
- Alterman RL, Stanley ER. Colony stimulating factor-1 expression in human glioma. Mol Chem Neuropathol. 1994;21:177–188. - PubMed
-
- Asano H, Aonuma M, Sanosaka T, Kohyama J, Namihira M, Nakashima K. Astrocyte differentiation of neural precursor cells is enhanced by retinoic acid through a change in epigenetic modification. Stem Cells. 2009;27:2744–2752. - PubMed
-
- Bangsow T, Baumann E, Bangsow C, Jaeger MH, Pelzer B, Gruhn P, Wolf S, von Melchner H, Stanimirovic DB. The epithelial membrane protein 1 is a novel tight junction protein of the blood-brain barrier. Journal of cerebral blood flow and metabolism : official journal of the International Society of Cerebral Blood Flow and Metabolism. 2008;28:1249–1260. - PubMed
-
- Barnabe-Heider F, Wasylnka JA, Fernandes KJ, Porsche C, Sendtner M, Kaplan DR, Miller FD. Evidence that embryonic neurons regulate the onset of cortical gliogenesis via cardiotrophin-1. Neuron. 2005;48:253–265. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases

