A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene
- PMID: 15944707
- PMCID: PMC4599349
- DOI: 10.1038/nature03552
A microRNA polycistron as a potential human oncogene
Abstract
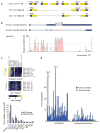
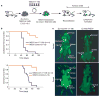
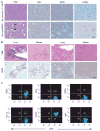
To date, more than 200 microRNAs have been described in humans; however, the precise functions of these regulatory, non-coding RNAs remains largely obscure. One cluster of microRNAs, the mir-17-92 polycistron, is located in a region of DNA that is amplified in human B-cell lymphomas. Here we compared B-cell lymphoma samples and cell lines to normal tissues, and found that the levels of the primary or mature microRNAs derived from the mir-17-92 locus are often substantially increased in these cancers. Enforced expression of the mir-17-92 cluster acted with c-myc expression to accelerate tumour development in a mouse B-cell lymphoma model. Tumours derived from haematopoietic stem cells expressing a subset of the mir-17-92 cluster and c-myc could be distinguished by an absence of apoptosis that was otherwise prevalent in c-myc-induced lymphomas. Together, these studies indicate that non-coding RNAs, specifically microRNAs, can modulate tumour formation, and implicate the mir-17-92 cluster as a potential human oncogene.
Conflict of interest statement
The authors declare no competing financial interests.
Figures
Comment in
-
Cancer genomics: small RNAs with big impacts.Nature. 2005 Jun 9;435(7043):745-6. doi: 10.1038/435745a. Nature. 2005. PMID: 15944682 No abstract available.
-
miRNAs, cancer, and stem cell division.Cell. 2005 Jul 15;122(1):6-7. doi: 10.1016/j.cell.2005.06.036. Cell. 2005. PMID: 16009126
References
-
- Ota A, et al. Identification and characterization of a novel gene, C13orf25, as a target for 13q31-q32 amplification in malignant lymphoma. Cancer Res. 2004;64:3087–3095. - PubMed
-
- Lee Y, et al. The nuclear RNase III Drosha initiates microRNA processing. Nature. 2003;425:415–419. - PubMed
-
- Bernstein E, Caudy AA, Hammond SM, Hannon GJ. Role for a bidentate ribonuclease in the initiation step of RNA interference. Nature. 2001;409:363–366. - PubMed
-
- Bartel DP. MicroRNAs: genomics, biogenesis, mechanism, and function. Cell. 2004;116:281–297. - PubMed
-
- Ambros V. The functions of animal microRNAs. Nature. 2004;431:350–355. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases
