The human oral microbiome
- PMID: 20656903
- PMCID: PMC2944498
- DOI: 10.1128/JB.00542-10
The human oral microbiome
Abstract
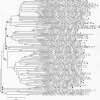
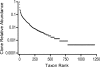
The human oral cavity contains a number of different habitats, including the teeth, gingival sulcus, tongue, cheeks, hard and soft palates, and tonsils, which are colonized by bacteria. The oral microbiome is comprised of over 600 prevalent taxa at the species level, with distinct subsets predominating at different habitats. The oral microbiome has been extensively characterized by cultivation and culture-independent molecular methods such as 16S rRNA cloning. Unfortunately, the vast majority of unnamed oral taxa are referenced by clone numbers or 16S rRNA GenBank accession numbers, often without taxonomic anchors. The first aim of this research was to collect 16S rRNA gene sequences into a curated phylogeny-based database, the Human Oral Microbiome Database (HOMD), and make it web accessible (www.homd.org). The HOMD includes 619 taxa in 13 phyla, as follows: Actinobacteria, Bacteroidetes, Chlamydiae, Chloroflexi, Euryarchaeota, Firmicutes, Fusobacteria, Proteobacteria, Spirochaetes, SR1, Synergistetes, Tenericutes, and TM7. The second aim was to analyze 36,043 16S rRNA gene clones isolated from studies of the oral microbiota to determine the relative abundance of taxa and identify novel candidate taxa. The analysis identified 1,179 taxa, of which 24% were named, 8% were cultivated but unnamed, and 68% were uncultivated phylotypes. Upon validation, 434 novel, nonsingleton taxa will be added to the HOMD. The number of taxa needed to account for 90%, 95%, or 99% of the clones examined is 259, 413, and 875, respectively. The HOMD is the first curated description of a human-associated microbiome and provides tools for use in understanding the role of the microbiome in health and disease.
Figures






References
-
- Aas, J. A., S. M. Barbuto, T. Alpagot, I. Olsen, F. E. Dewhirst, and B. J. Paster. 2007. Subgingival plaque microbiota in HIV positive patients. J. Clin. Periodontol. 34:189-195. - PubMed
-
- Awano, S., T. Ansai, Y. Takata, I. Soh, S. Akifusa, T. Hamasaki, A. Yoshida, K. Sonoki, K. Fujisawa, and T. Takehara. 2008. Oral health and mortality risk from pneumonia in the elderly. J. Dent. Res. 87:334-339. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Molecular Biology Databases

