Genetic variability of respiratory syncytial viruses (RSV) prevalent in Southwestern China from 2006 to 2009: emergence of subgroup B and A RSV as dominant strains
- PMID: 20147636
- PMCID: PMC2849604
- DOI: 10.1128/JCM.02258-09
Genetic variability of respiratory syncytial viruses (RSV) prevalent in Southwestern China from 2006 to 2009: emergence of subgroup B and A RSV as dominant strains
Abstract
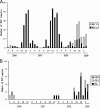
Respiratory syncytial virus (RSV) is the most commonly identified viral agent in young children with acute respiratory tract infections (ARIs) and often causes repeated infections throughout life. This study investigated the genetic variability of the attachment (G) protein gene among RSV strains prevalent in southwestern China. Reverse transcription-PCR (RT-PCR) for a fragment of the RSV G gene was performed with nasopharyngeal aspirates (NPAs) collected from children with ARIs hospitalized in Chongqing Children's Hospital, Chongqing, China. A total of 1,387 NPA specimens were collected from April 2006 to March 2009, and 439 (31.7%) were positive for RSV. During the study period, subgroup A and B viruses accounted for 79.5% (349/439) and 19.8% (87/439) of the total positive samples, respectively. Both subgroup A and B viruses were identified in three samples. Subgroup A viruses were predominant during two epidemic seasons (2006 to 2008), while subgroup B strains prevailed during the 2008-2009 epidemic season. Phylogenetic analyses showed that all 30 group A strains could be clustered into one genotype, genotype GA2, and 30 group B strains could be clustered into three genotypes, genotypes GB1, GB3, and BA, among which 17 genotype BA strains were detected from 23 group B strains selected during the 2008-2009 epidemic season. The G gene of genotype BA was predicted to encode proteins of five different lengths. These data suggest that group A RSV likely predominated in southwestern China and that a new genotype of subgroup B with a 60-nucleotide insertion, named BA-like virus, became the dominant genotype in the 2008-2009 epidemic season.
Figures


References
-
- Agrawal, A. S., M. Sarkar, S. Ghosh, M. Chawla-Sarkar, N. Chakraborty, M. Basak, and T. N. Naik. 2009. Prevalence of respiratory syncytial virus group B genotype BA-IV strains among children with acute respiratory tract infection in Kolkata, Eastern India. J. Clin. Virol. 45:358-361. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, L. J., J. C. Hierholzer, C. Tsou, R. M. Hendry, B. F. Fernie, Y. Stone, and K. McIntosh. 1985. Antigenic characterization of respiratory syncytial virus strains with monoclonal antibodies. J. Infect. Dis. 151:626-633. - PubMed
-
- Arbiza, J., A. Delfraro, and S. Frabasile. 2005. Molecular epidemiology of human respiratory syncytial virus in Uruguay: 1985-2001—a review. Mem. Inst. Oswaldo Cruz 100:221-230. - PubMed
-
- Cane, P. A., and C. R. Pringle. 1995. Molecular epidemiology of respiratory syncytial virus: a review of the use of reverse transcription-polymerase chain reaction in the analysis of genetic variability. Electrophoresis 16:329-333. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

