Anti-influenza serum and mucosal antibody responses after administration of live attenuated or inactivated influenza vaccines to HIV-infected children
- PMID: 20581690
- PMCID: PMC3290334
- DOI: 10.1097/QAI.0b013e3181e46308
Anti-influenza serum and mucosal antibody responses after administration of live attenuated or inactivated influenza vaccines to HIV-infected children
Abstract
Background: Live-attenuated influenza vaccine (LAIV) prevents more cases of influenza in immune-competent children than the trivalent inactivated vaccine (TIV). We compared the antibody responses to LAIV or TIV in HIV-infected children.
Methods: Blood and saliva obtained at enrollment, 4 and 24 weeks postimmunization from 243 HIV-infected children randomly assigned to TIV or LAIV were analyzed.
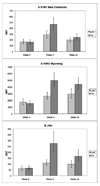
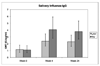
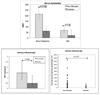
Results: Both vaccines increased the anti-influenza neutralizing antibodies at 4 and 24 weeks postimmunization. At 4 weeks postimmunization, TIV recipients had 2-fold to 3-fold higher neutralizing antibody titers than LAIV recipients, but the proportions of subjects with protective titers (≥ 1:40) were similar between treatment groups (96%-100% for influenza A and 81%-88% for influenza B). Both vaccines increased salivary homotypic IgG antibodies, but not IgA antibodies. Both vaccines also increased serum heterosubtypic antibodies. Among HIV-specific characteristics, the baseline viral load correlated best with the antibody responses to either vaccine. We used LAIV-virus shedding as a surrogate of influenza infection. Influenza-specific humoral and mucosal antibody levels were significantly higher in nonshedders than in shedders.
Conclusions: LAIV and TIV generated homotypic and heterosubtypic humoral and mucosal antibody responses in HIV-infected children. High titers of humoral or mucosal antibodies correlated with protection against viral shedding.
Figures
References
-
- Fiore AE, Shay DK, Broder K, et al. Prevention and control of seasonal influenza with vaccines: recommendations of the Advisory Committee on Immunization Practices (ACIP), 2009. MMWR Recomm Rep. 2009 Jul 31;58(RR-8):1–52. - PubMed
-
- Yamanaka H, Teruya K, Tanaka M, et al. Efficacy and immunologic responses to influenza vaccine in HIV-1-infected patients. J Acquir Immune Defic Syndr. 2005 Jun 1;39(2):167–173. - PubMed
-
- Amendola A, Boschini A, Colzani D, et al. Influenza vaccination of HIV-1-positive and HIV-1-negative former intravenous drug users. J Med Virol. 2001 Dec;65(4):644–648. - PubMed
-
- Iorio AM, Alatri A, Francisci D, et al. Immunogenicity of influenza vaccine (1993–94 winter season) in HIV-seropositive and -seronegative ex-intravenous drug users. Vaccine. 1997 Jan;15(1):97–102. - PubMed
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Grants and funding
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Medical
Miscellaneous

