Stimulation of methane generation from nonproductive coal by addition of nutrients or a microbial consortium
- PMID: 20817801
- PMCID: PMC2976240
- DOI: 10.1128/AEM.00728-10
Stimulation of methane generation from nonproductive coal by addition of nutrients or a microbial consortium
Abstract
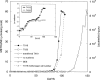
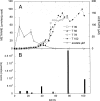
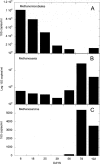
Biogenic formation of methane from coal is of great interest as an underexploited source of clean energy. The goal of some coal bed producers is to extend coal bed methane productivity and to utilize hydrocarbon wastes such as coal slurry to generate new methane. However, the process and factors controlling the process, and thus ways to stimulate it, are poorly understood. Subbituminous coal from a nonproductive well in south Texas was stimulated to produce methane in microcosms when the native population was supplemented with nutrients (biostimulation) or when nutrients and a consortium of bacteria and methanogens enriched from wetland sediment were added (bioaugmentation). The native population enriched by nutrient addition included Pseudomonas spp., Veillonellaceae, and Methanosarcina barkeri. The bioaugmented microcosm generated methane more rapidly and to a higher concentration than the biostimulated microcosm. Dissolved organics, including long-chain fatty acids, single-ring aromatics, and long-chain alkanes accumulated in the first 39 days of the bioaugmented microcosm and were then degraded, accompanied by generation of methane. The bioaugmented microcosm was dominated by Geobacter sp., and most of the methane generation was associated with growth of Methanosaeta concilii. The ability of the bioaugmentation culture to produce methane from coal intermediates was confirmed in incubations of culture with representative organic compounds. This study indicates that methane production could be stimulated at the nonproductive field site and that low microbial biomass may be limiting in situ methane generation. In addition, the microcosm study suggests that the pathway for generating methane from coal involves complex microbial partnerships.
Figures



References
-
- Anderson, R. T., and D. R. Lovley. 2000. Hexadecane decay by methanogenesis. Nature 404:722-723. - PubMed
-
- Anderson, R. T., J. N. Rooney-Varga, C. V. Gaw, and D. R. Lovley. 1998. Anaerobic benzene oxidation in the Fe(III) reduction zone of petroleum-contaminated aquifers. Environ. Sci. Technol. 32:1222-1229.
-
- Bakermans, C., and E. L. Madsen. 2002. Diversity of 16S rDNA and naphthalene dioxygenase genes from coal-tar-waste-contaminated aquifer waters. Microb. Ecol. 44:95-106. - PubMed
-
- Breland, F. C., Jr. 2004. Coalbed methane potential in Louisiana, p. 27-35. In P. D. Warwick (ed.), Selected presentations on coal-bed gas in the eastern United States. U.S. Geological Survey Open-File Report 2004-1273. U.S. Geological Survey, Reston, VA.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Other Literature Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

