Phylogeographic pattern of the striped snakehead, Channa striata in Sundaland: ancient river connectivity, geographical and anthropogenic signatures [corrected]
- PMID: 23284881
- PMCID: PMC3527338
- DOI: 10.1371/journal.pone.0052089
Phylogeographic pattern of the striped snakehead, Channa striata in Sundaland: ancient river connectivity, geographical and anthropogenic signatures [corrected]
Erratum in
- PLoS One. 2013;8(5). doi:10.1371/annotation/2be4a0a9-b3ed-492f-8c4d-15d3a5ae6cab
Abstract
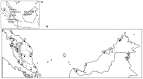
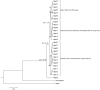
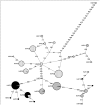
A phylogeographic study of an economically important freshwater fish, the striped snakehead, Channa striata in Sundaland was carried out using data from mtDNA ND5 gene target to elucidate genetic patterning. Templates obtained from a total of 280 individuals representing 24 sampling sites revealed 27 putative haplotypes. Three distinct genetic lineages were apparent; 1)northwest Peninsular Malaysia, 2)southern Peninsular, east Peninsular, Sumatra and SW (western Sarawak) and 3) central west Peninsular and Malaysian Borneo (except SW). Genetic structuring between lineages showed a significant signature of natural geographical barriers that have been acting as effective dividers between these populations. However, genetic propinquity between the SW and southern Peninsular and east Peninsular Malaysia populations was taken as evidence of ancient river connectivity between these regions during the Pleistocene epoch. Alternatively, close genetic relationship between central west Peninsular Malaysia and Malaysian Borneo populations implied anthropogenic activities. Further, haplotype sharing between the east Peninsular Malaysia and Sumatra populations revealed extraordinary migration ability of C. striata (>500 km) through ancient connectivity. These results provide interesting insights into the historical and contemporary landscape arrangement in shaping genetic patterns of freshwater species in Sundaland.
Conflict of interest statement
Figures
References
-
- Lande R (1998) Anthropogenic, ecological and genetic factors in extinction and conservation. Researches on Population Ecology 40(3): 259–269.
-
- Turner TF, McPhee MV, Campbell P, Winemiller KO (2004) Phylogeography and intraspecific genetic variation of prochilodontid fishes endemic to rivers of northern South America. Journal of Fish Biology 64: 186–201.
-
- Voris HK (2000) Map of Pleistocene sea levels in Southeast Asia: shorelines, river systems and time duration. Journal of Biogeography 27: 1153–1167.
-
- Kamarudin KR, Esa Y (2009) Phylogeny and phylogeography of Barbonymus schwanenfeldii (Cyprinidae) from Malaysia inferred using partial cytochrome b mtDNA gene. Journal of Tropical Biology and Conservation 5: 1–13.
-
- Mohsin AKM, Ambak MA (1983) Freshwater fishes of Peninsular Malaysia. Kuala Lumpur: Penerbitan Universiti Pertanian Malaysia. 284p.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources

