Composition of the summer photosynthetic pico and nanoplankton communities in the Beaufort Sea assessed by T-RFLP and sequences of the 18S rRNA gene from flow cytometry sorted samples
- PMID: 22278671
- PMCID: PMC3400408
- DOI: 10.1038/ismej.2011.213
Composition of the summer photosynthetic pico and nanoplankton communities in the Beaufort Sea assessed by T-RFLP and sequences of the 18S rRNA gene from flow cytometry sorted samples
Abstract
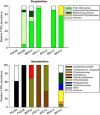
The composition of photosynthetic pico and nanoeukaryotes was investigated in the North East Pacific and the Arctic Ocean with special emphasis on the Beaufort Sea during the MALINA cruise in summer 2009. Photosynthetic populations were sorted using flow cytometry based on their size and pigment fluorescence. Diversity of the sorted photosynthetic eukaryotes was determined using terminal-restriction fragment length polymorphism analysis and cloning/sequencing of the 18S ribosomal RNA gene. Picoplankton was dominated by Mamiellophyceae, a class of small green algae previously included in the prasinophytes: in the North East Pacific, the contribution of an Arctic Micromonas ecotype increased steadily northward becoming the only taxon occurring at most stations throughout the Beaufort Sea. In contrast, nanoplankton was more diverse: North Pacific stations were dominated by Pseudo-nitzschia sp. whereas those in the Beaufort Sea were dominated by two distinct Chaetoceros species as well as by Chrysophyceae, Pelagophyceae and Chrysochromulina spp.. This study confirms the importance of Arctic Micromonas within picoplankton throughout the Beaufort Sea and demonstrates that the photosynthetic picoeukaryote community in the Arctic is much less diverse than at lower latitudes. Moreover, in contrast to what occurs in warmer waters, most of the key pico- and nanoplankton species found in the Beaufort Sea could be successfully established in culture.
Figures







References
-
- Assmy P, Hernandez-Becerril DU, Montresor M. Morphological variability and life cycle traits of the type species of the diatom genus Chaetoceros, C. dichaeta. J Phycol. 2008;44:152–163. - PubMed
-
- Baldwin AJ, Moss JA, Pakulski JD, Catala P, Joux F, Jeffrey WH. Microbial diversity in a Pacific Ocean transect from the Arctic to Antarctic circles. Aquat Microb Ecol. 2005;41:91–102.
-
- Balzano S, Sarno D, Kooistra W. Effects of salinity on the growth rate and morphology of ten Skeletonema strains. J Plankton Res. 2011;33:937–945.
-
- Booth BC, Horner RA. Microalgae on the Arctic Ocean Section, 1994: species abundance and biomass. Deep-Sea Res II-Topical Stud Oceanogr. 1997;44:1607–1622.
-
- Booth BC, Larouche P, Belanger S, Klein B, Amiel D, Mei ZP. Dynamics of Chaetoceros socialis blooms in the North Water. Deep-Sea Res II-Topical Stud Oceanogr. 2002;49:5003–5025.
Publication types
MeSH terms
Substances
Associated data
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
- Actions
LinkOut - more resources
Full Text Sources
Molecular Biology Databases
Miscellaneous

